Home > Press > Visible light and nanoparticle catalysts produce desirable bioactive molecules: Simple photochemical method takes advantage of quantum mechanics
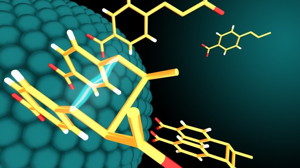 |
| Nanoparticle catalysts and light drive a reaction that produces bioactive molecules. |
Abstract:
•Arrangement of atoms in molecules is most relevant for drug companies
•Nanoparticles are only three nanometers wide
•Catalysts can be reused for more chemical reactions
Visible light and nanoparticle catalysts produce desirable bioactive molecules: Simple photochemical method takes advantage of quantum mechanics
Evanston, IL | Posted on October 31st, 2019Northwestern University chemists have used visible light and extremely tiny nanoparticles to quickly and simply make molecules that are of the same class as many lead compounds for drug development.
Driven by light, the nanoparticle catalysts perform chemical reactions with very specific chemical products -- molecules that don’t just have the right chemical formulas but also have specific arrangements of their atoms in space. And the catalyst can be reused for additional chemical reactions.
The semiconductor nanoparticles are known as quantum dots -- so small that they are only a few nanometers across. But the small size is power, providing the material with attractive optical and electronic properties not possible at greater length scales.
“Quantum dots behave more like organic molecules than metal nanoparticles,” said Emily A. Weiss, who led the research. “The electrons are squeezed into such a small space that their reactivity follows the rules of quantum mechanics. We can take advantage of this, along with the templating power of the nanoparticle surface.”
This work, published recently by the journal Nature Chemistry, is the first use of a nanoparticle’s surface as a template for a light-driven reaction called a cycloaddition, a simple mechanism for making very complicated, potentially bioactive compounds.
“We use our nanoparticle catalysts to access this desirable class of molecules, called tetrasubstituted cyclobutanes, through simple, one-step reactions that not only produce the molecules in high yield, but with the arrangement of atoms most relevant for drug development,” Weiss said. “These molecules are difficult to make any other way.”
Weiss is the Mark and Nancy Ratner Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. She specializes in controlling light-driven electronic processes in quantum dots and using them to perform light-driven chemistry with unprecedented selectivity.
The nanoparticle catalysts use energy from visible light to activate molecules on their surfaces and fuse them together to form larger molecules in configurations useful for biological applications. The larger molecule then detaches easily from the nanoparticle, freeing the nanoparticle to be used again in another reaction cycle.
In their study, Weiss and her team used three-nanometer nanoparticles made of the semiconductor cadmium selenide and a variety of starter molecules called alkenes in solution. Alkenes have core carbon-carbon double bonds which are needed to form the cyclobutanes.
The study is titled “Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots.” Yishu Jiang, a graduate student in Weiss’ lab, is the study’s first author.
The research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (grant 9550-17-1-0271) and by the Center for Bio-Inspired Energy Science, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences (award no. DE-SC0000989).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman at 847-491-3115 or
Source contact: Emily Weiss at
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








