Home > Press > Can't get thinner than this: synthesis of atomically flat boron sheets
 |
Abstract:
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) find a simple method for producing atomically thin layers of oxidized borophene, a promising 2D boron-based nanomaterial that could serve in a variety of fields.
Can't get thinner than this: synthesis of atomically flat boron sheets
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on August 23rd, 2019Since its rediscovery and characterization in 2004, graphene has been the focus of countless research efforts across multiple fields. It is a very versatile material consisting of a two-dimensional (2D) carbon network; in other words, it comprises a thin sheet of carbon that has a thickness of one atom. Graphene is not only stronger than the strongest steels, but also has a myriad of interesting chemical, electronic, and mechanical characteristics that has left scientists wondering if similar 2D networks of other materials could have such useful properties.
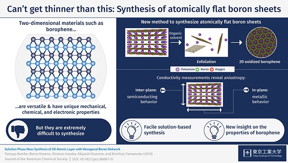
One novel 2D material that was recently reported is borophene, an analogue of graphene but consisting of boron atoms instead of carbon atoms. However, as one would expect for 2D sheets of any material, the synthesis of borophene has proved to be challenging. Researchers either require the use of a substrate to make borophene more stable or coupling boron with hydroxyl groups (OH-), which causes the structure to not be atomically flat.
In a recent study conducted at Tokyo Institute of Technology, a research team including Tetsuya Kambe, Akiyoshi Kuzume and Kimihisa Yamamoto was successful in synthesizing atomically flat oxidized borophene sheets through a simple solution-based method. First, they synthesized stacked layers of borophene oxide through a fairly simple process using a potassium borohydride salt (KBH4). An X-ray analysis revealed the 2D-layered structure of the material, in which layers of boron atoms forming a hexagonal 2D network with oxygen atoms as bridges were intercalated with layers containing potassium atoms. Then, the subsequent necessary step was to find a way to exfoliate atomically thin layers of the borophene oxide network. The researchers achieved this by putting the material in dimethylformamide, which is a commonly used organic solvent. Various types of measurements were carried out to verify the structure of the exfoliated sheets, including electron microscopy, spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy. The results confirmed that the proposed method was effective for producing the desired atomically flat oxidized borophene sheets.
Finally, the researchers performed resistivity measurements to analyze the conducting properties of stacked borophene sheets and found an interesting characteristic referred to as anisotropy. This means that the sheets exhibited different types of conductivity depending on the direction of the current flow. The material behaved like a semiconductor in the inter-plane direction, whereas it exhibited metal-like behavior in the in-plane direction of the boron network. The mechanisms behind these two types of conducting behaviors were elucidated as well. "It is important to note that our boron sheets can be handled easily at ambient conditions," remarks Dr. Kambe, indicating that this pioneering research could be the basis for finding potential applications for borophene.
Finding facile methods for the synthesis of borophene and borophene-based compounds is crucial to conducting further research on this interesting material and its potential uses. "Like graphene, borophene is expected to have unique properties, including extraordinary mechanical characteristics and metallic behavior that could be exploited in a variety of fields," states Dr. Kambe. Hopefully, future findings and developments on 2D materials will enable us to employ their exotic properties and tailor them to suit our needs.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Assistant Professor Tetsuya Kambe
Institute of Innovative Research
Email
Tel +81-45-924-5259
Contact
Public Relations Section, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Email
Tel +81-3-5734-2975
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Thin films
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








