Home > Press > Research brief: A novel cellular process to engulf nano-sized materials
 |
| Credit: Hongbo Pang. |
Abstract:
Nanometers are one billionth of a meter, a metric typically used to measure molecules and scientific building blocks not visible to the human eye. Materials of tens and/or several hundred nanometers in diameter have unique properties, and thus have been widely used in diagnosing and treating various human diseases. One major challenge to use these nano-sized materials is how to deliver them into cells and reach their sites of action.
Research brief: A novel cellular process to engulf nano-sized materials
Minneapolis, MN | Posted on August 20th, 2019Traditional methods include linking them to short fragments of proteins called peptides, which are structural components of cells and tissues, hormones, toxins, antibiotics and enzymes. These peptides, by interacting with cells, will lead nanomaterial into cells. The impact of these interactions on other cellular activities remains poorly understood, plus this peptide coupling introduces additional complexity in nanomaterial manufacturing, and may change their functionality as well.
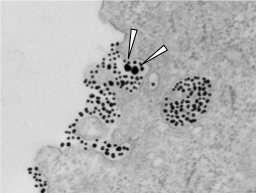
In a study published in Nature Communications, University of Minnesota researchers discovered a novel cellular process that can engulf nanomaterial without direct peptide functionalization, and its activity is regulated by Cysteine surrounding the cells. The research team termed this cellular process of engulfing bystander NPs as 'bystander uptake.'
"By simply mixing two types of nano-sized material, we discover a novel cellular process that offers an easy solution for nanomaterial entry into cells," said Hongbo Pang, corresponding author, an assistant professor in the College of Pharmacy and a member of the Masonic Cancer Center. "Moreover, it opens up a new avenue of cell biology that interconnects several fundamental elements of living cells. Further understanding of this process will aid in both cell biology and nanotechnology development."
The study revealed the following unique properties:
the bystander uptake only allows the cells to engulf nano-sized materials, but not other substances surrounding the cells (e.g. fluids);
the activity of this bystander uptake is stimulated by the existence of one of 20 natural amino acids, Cysteine, surrounding the cells.
These phenomena have been validated with a wide variety of cells, nanoparticles (aka nanomaterials), and under various physiological conditions.
The study findings included:
co-administration with TAT-NP, a peptide and nanomaterial fusion, enables cells to engulf nano-sized materials in a bystander manner;
this bystander uptake is specific to nanomaterial, but not other substances surrounding the cells;
cysteine in the cell culture medium greatly stimulates the activity of this bystander uptake.
###
This study was funded by NIBIB (National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering), NCI (National Cancer Institute) and the BICI (Beijing Institute of Collaborative Innovation).
####
About University of Minnesota
About the College of Pharmacy
Founded in 1892, the University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy is the only pharmacy school in Minnesota, with campuses in the Twin Cities and in Duluth. The College of Pharmacy improves health through innovative education, pioneering research and interdisciplinary practice development that attends to the diverse needs of the people of Minnesota and the world.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Katrinna Dodge
612-624-4071
Copyright © University of Minnesota
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Cancer
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








