Home > Press > IMDEA Nanociencia and Universidad Autónoma de Madrid researchers have demonstrated that graphene deposited on a metal surface promotes an unusual chemical reaction that would hardly take place under noncatalyzed conditions.
 |
| Image of TCNQ-CH2CN molecule on a corrugated graphene layer (left) and representation of the calculated geometries (right). Adapted from Navarro et al. Sci. Adv. 2018. |
Abstract:
Graphene monolayers can be epitaxially grown on many single-crystal metal surfaces under ultra-high vacuum. On one side, these monolayers protect highly reactive metallic surfaces from contaminants, but on the other side, the piling of the layers as graphitic carbon poisons the activity of transition metal catalysts. The inertness of the graphite and the physical blockage of the active sites prevents chemical reactions occurring on the metal surface.
IMDEA Nanociencia and Universidad Autónoma de Madrid researchers have demonstrated that graphene deposited on a metal surface promotes an unusual chemical reaction that would hardly take place under noncatalyzed conditions.
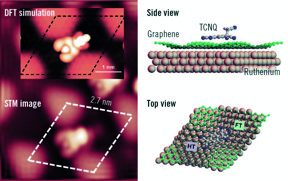
Madrid, Spain | Posted on December 14th, 2018Researchers led by Fernando Martín, Emilio Pérez and Amadeo Vázquez de Parga (IMDEA Nanociencia and Universidad Autónoma de Madrid) have demonstrated that nanostructured graphene monolayers on a metal surface do promote a chemical reaction that would hardly take place under noncatalyzed conditions. A crystal of ruthenium, Ru(0001), has been covered with an epitaxially grown continuous graphene layer. Because of the difference in lattice parameters, a new superperiodicity appears on the graphene layer and modulates its electronic properties. Taking advantage of the modulation, the surface has been functionalized with cyanomethylene groups (-CH2CN), covalently bonded to the center of the hexagonal close-packed areas in the Moiré unit cell, and doped with TCNQ (7,7,8,8-tetracyano-p-quinodimethane). TCNQ is an electron acceptor molecule used to p-dope graphene films. When deposited on the graphene surface, this molecule is absorbed on a bridge position between two ripples. Here, it is worth to notice the important role of the surface and of the graphene layer in catalyzing the reaction of TCNQ and -CH2CN. The reaction of TCNQ with CH3CN (the pristine reactants are in gas phase) plus the loss of a hydrogen atom is very unlikely because of the high energy barrier (about 5 eV). The presence of the graphene layer reduces this energy barrier by a factor of 5, thus favoring the formation of the products.
The nanostructured graphene promotes the reaction in a threefold way: first, holds the -CH2CN in place; second, allows for an efficient charge transfer from the ruthenium; and third, prevents the absorption of TCNQ by ruthenium allowing the molecule to diffuse on the surface. “A similar clean reaction on pristine ruthenium is not possible, because the reactive character of ruthenium leads to the absorption of CH3CN and hinders the mobility of TCNQ molecules once absorbed on the surface” Amadeo says. The results confirm the catalytic character of graphene in this reaction. “Such a selectivity would be difficult to obtain by using other forms of carbon” Emilio confirms.
Further, the TCNQ molecules have been injected with electrons using the scanning tunneling microscope (STM). This individual manipulation of the molecules induces a C-C bond breaking, thus leading to the recovery of the initial reactants: CH2CN-graphene and TCNQ. The process is reversible and reproducible at a single-molecule level. As the researchers have observed a Kondo resonance, the reversibility of the process can be thought as a reversible magnetic switch controlled by a chemical reaction.
Fernando Martín, Emilio Pérez and Amadeo Vázquez de Parga are researchers at the Madrid’s Institute of Advanced Studies IMDEA Nanociencia. The work is a collaboration between IMDEA Nanociencia and Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, and the Condensed Matter Physics Center IFIMAC. The research has been co-funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, the Government of the Region of Madrid and the European Research Council.
Article:
J. Navarro, M. Pisarra, B. Nieto-Ortega, J. Villalva, C. G. Ayani, C. Díaz, F. Calleja, R. Miranda, F. Martín, E. M. Pérez, A. L. Vázquez de Parga. Graphene catalyzes the reversible formation of a C–C bond between two molecules. Sci. Adv. 4, eaau9366 (2018).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Prof. Emilio Pérez
emilio.perez [at] imdea.org
http://www.nanociencia.imdea.org/home-en/people/item/emilio-perez-alvarez
Twitter: @emilioperezlab
Prof. Amadeo L. Vázquez de Parga
al.vazquezdeparga [at] uam.es
http://nanociencia.imdea.org/nanoscale-imaging-of-2d-materials/group-home
Comunicación científica IMDEA Nanociencia
divulgacion.nanociencia [at] imdea.org
+34 91 299 87 12
Twitter: @IMDEA_nano,
Facebook: @IMDEANanociencia
Copyright © IMDEA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








