Home > Press > World's fastest man-made spinning object could help study quantum mechanics
 |
| A nanodumbbell levitated by an optical tweezer in vacuum can vibrate or spin, depending on the polarization of the incoming laser. (Purdue University photo/Tongcang Li) |
Abstract:
Optically Levitated Nanodumbbell Torsion Balance and GHz Nanomechanical Rotor
Jonghoon Ahn, Zhujing Xu, Jaehoon Bang, Yu-Aao Deng, Thai M. Hoang, Qinkai Han, Ren-Min Ma, Tongcang Li
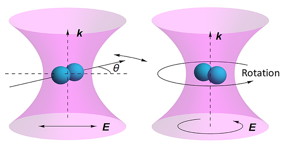
Levitated optomechanics has great potential in precision measurements, thermodynamics, macroscopic quantum mechanics, and quantum sensing. Here we synthesize and optically levitate silica nanodumbbells in high vacuum. With a linearly polarized laser, we observe the torsional vibration of an optically levitated nanodumbbell. This levitated nanodumbbell torsion balance is a novel analog of the Cavendish torsion balance, and provides rare opportunities to observe the Casimir torque and probe the quantum nature of gravity as proposed recently. With a circularly polarized laser, we drive a 170-nm-diameter nanodumbbell to rotate beyond 1 GHz, which is the fastest nanomechanical rotor realized to date. Smaller silica nanodumbbells can sustain higher rotation frequencies. Such ultrafast rotation may be used to study material properties and probe vacuum friction.
The video was prepared by Erin Easterling, digital producer for the Purdue College of Engineering, 765-496-3388, easterling@purdue.edu.
World's fastest man-made spinning object could help study quantum mechanics
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on July 20th, 2018Researchers have created the fastest man-made rotor in the world, which they believe will help them study quantum mechanics.
At more than 60 billion revolutions per minute, this machine is more than 100,000 times faster than a high-speed dental drill.
"This study has many applications, including material science," said Tongcang Li, an assistant professor of physics and astronomy, and electrical and computer engineering, at Purdue University. "We can study the extreme conditions different materials can survive in."
Li's team synthesized a tiny dumbbell from silica and levitated it in high vacuum using a laser. The laser can work in a straight line or in a circle - when it's linear, the dumbbell vibrates, and when it's circular, the dumbbell spins.
A spinning dumbbell functions as a rotor, and a vibrating dumbbell functions like an instrument for measuring tiny forces and torques, known as a torsion balance. These devices were used to discover things like the gravitational constant and density of Earth, but Li hopes that as they become more advanced, they'll be able to study things like quantum mechanics and the properties of vacuum. Watch a video to see how it happens here.
"People say that there is nothing in vacuum, but in physics, we know it's not really empty," Li said. "There are a lot of virtual particles which may stay for a short time and then disappear. We want to figure out what's really going on there, and that's why we want to make the most sensitive torsion balance."
By observing this tiny dumbbell spin faster than anything before it, Li's team may also be able to learn things about vacuum friction and gravity. Understanding these mechanisms is an essential goal for the modern generation of physics, Li said.
###
Researchers from Purdue, Peking University, Tsinghua University, and the Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter in Beijing also contributed to this work. The first author of this work is Jonghoon Ahn, a graduate student in Li's research group. Li's research was funded by the National Science Foundation and Office of Naval Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer: Kayla Zacharias
765-494-9318
Source: Tongcang Li
765-496-0072
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








