Home > Press > High-speed and on-silicon-chip graphene blackbody emitters: Integrated light emitters for optical communications
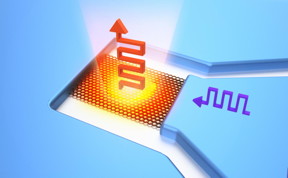 |
| Square graphene sheet is connected to source and drain electrodes. Modulated blackbody emission is obtained from graphene by applying input signal. CREDIT Keio University |
Abstract:
Graphene is a two-dimensional nanocarbon material, having unique properties in electronic, optical and thermal properties, which can be applied for optoelectronic devices. Graphene-based blackbody emitters are also promising light emitters on silicon chip in NIR and mid-infrared region. However, although graphene-based blackbody emitters have been demonstrated under steady-state conditions or relatively slow modulation (100 kHz), the transient properties of these emitters under high-speed modulation have not been reported to date. Also, the optical communications with graphene-based emitters have never been demonstrated.
High-speed and on-silicon-chip graphene blackbody emitters: Integrated light emitters for optical communications
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on April 5th, 2018Here, a highly integrated, high-speed and on-chip blackbody emitter based on graphene in NIR region including telecommunication wavelength was demonstrated. A fast response time of ~ 100 ps, which is ~ 105 higher than the previous graphene emitters, has been experimentally demonstrated for single and few-layer graphene, the emission responses can be controlled by the graphene contact with the substrate depending on the number of graphene layers. The mechanisms of the high-speed emission are elucidated by performing theoretical calculations of the heat conduction equations considering the thermal model of emitters including graphene and a substrate. The simulated results indicate that the fast response properties can be understood not only by the classical thermal transport of in-plane heat conduction in graphene and heat dissipation to the substrate but also by the remote quantum thermal transport via the surface polar phonons (SPoPhs) of the substrates. In addition, first real-time optical communication with graphene-based light emitters was experimentally demonstrated, indicating that graphene emitters are novel light sources for optical communication. Furthermore, we fabricated integrated two-dimensional array emitters with large-scale graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) method and capped emitters operable in air, and carried out the direct coupling of optical fibers to the emitters owing to their small footprint and planar device structure.
Graphene light emitters are greatly advantageous over conventional compound semiconductor emitters because they can be highly integrated on silicon chip due to simple fabrication processes of graphene emitters and direct coupling with silicon waveguide through an evanescent field. Because graphene can realize high-speed, small footprint and on-Si-chip light emitters, which are still challenges for compound semiconductors, the graphene-based light emitters can open new routes to highly integrated optoelectronics and silicon photonics.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hideyuki Maki
81-455-661-643
Copyright © Japan Science and Technology Agency
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








