Home > Press > Promising sensors for submarines, mines and spacecraft: MSU scientists are developing nanostructured gas sensors that would work at room temperature
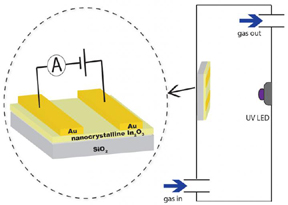 |
| This is a hydrogen sensor scheme. CREDIT Alexander Ilyin |
Abstract:
Researchers from the Physics Department of Moscow State University and their colleagues have discovered a mechanism that allows gas sensors, based on nanocrystalline metal oxides, to work at room temperature. This invention will raise the efficiency of environmental monitoring at nuclear power plants, on submarines and spacecrafts. The discovery was reported in Scientific Reports.
Promising sensors for submarines, mines and spacecraft: MSU scientists are developing nanostructured gas sensors that would work at room temperature
Moscow, Russia | Posted on November 10th, 2017Scientists have proposed a new fundamental principle of operation of hydrogen sensors. Unlike most resistive gas detectors, it does not need to be heated and only requires visible light. This discovery will significantly reduce the energy consumption of the sensor and expand its scope.
"Such sensors can be used in explosive environments or be built into mobile devices without constructing additional heat sink systems," said Alexander Ilyin, a co-author of the study, a PhD student at the Physics Department of Moscow State University.
Researchers have found out that composites based on zinc and indium oxides can significantly increase the sensitivity of the sensor to hydrogen. Physicists have also proposed an explanation for the hypersensitivity of the designed composite. In their opinion, the sensor response mechanism consists in a change in the processes of generation and recombination of nonequilibrium electrons when the composite is interacting with hydrogen. Composites with a certain structure provide a more significant change in these processes.
Samples for the sensor were made from nanocrystalline indium and zinc oxide powders. The structure and particle size were studied by the means of transmission electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction. The electrical and sensor characteristics of the structureswere studied in the new designed setup, in which the required temperature of the composite and the concentration of hydrogen were well controlled.
The obtained results would allow the scientists to develop a new type of resistive hydrogen sensor that works under additional illumination without heating. Such sensors are promising not only for effective monitoring of environmental pollution in industrial plants, but also for constant monitoring of air in closed facilities (submarines, mines, spacecraft) where the slightest change in the chemical composition can lead to human casualties.
###
The research was carried out jointly with the scientists of N.N. Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics RAS, National Research Center «Kurchatov Institute» (NRCKI) and Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry (NIFKhI).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yana Khlyustova
Copyright © Lomonosov Moscow State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Mining/Extraction/Drilling
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Marine/Watercraft
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








