Home > Press > Sensing technology takes a quantum leap with RIT photonics research: Office of Naval Research funds levitated optomechanics project
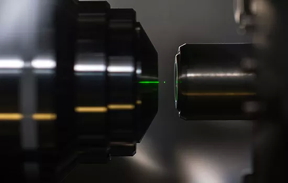 |
| J. Adam Fenster and Prof. A. N. Vamivakas, University of Rochester It’s no trick of the eye; it’s an optical trap. Levitated optomechanics can make a nanoparticle float in space. A finely focused laser beam forms an “optical tweezer” and creates a tiny, isolated laboratory for the study of delicate quantum states. RIT scientist Mishkat Bhattacharya tests his theoretical predictions on such experimental platforms used by his collaborator Nick Vamivakas at the University of Rochester’s Institute of Optics. |
Abstract:
Research underway at RIT advances a new kind of sensing technology that captures data with better precision than currently possible and promises cheaper, smaller and lighter sensor designs.
Sensing technology takes a quantum leap with RIT photonics research: Office of Naval Research funds levitated optomechanics project
Rochester, NY | Posted on August 10th, 2017Mishkat Bhattacharya, a theoretical physicist at RIT, is investigating new precision quantum sensing solutions for the U.S. Department of the Navy’s Office of Naval Research. The three-year study is supported by $550,000 grant and is a continuation of a previous award. Bhattacharya will test interactions between light and matter at the nanoscale and analyze measurements of weak electromagnetic fields and gravitational forces.
Specialized microscopes measure theoretical predictions that describe matter at the nanoscale in which a nanometer equals one-billionth of a meter and a human hair measures between 80,000-100,000 nanometers, according to the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative.
Bhattacharya works in the emerging field of levitated optomechanics, an area of physics that investigates nanoparticles by trapping them in a laser beam. Laser trapping—a method known as “optical tweezers”—tests the limits of quantum effects in isolation and eliminates physical disturbances from the surrounding environment
Using the techniques of laser trapping, Bhattacharya takes quantum mechanics to the next level by probing quantum effects in the nanoparticles, which contain billions of atoms. He investigates where quantum mechanics (which governs the microscopic) butts up against classical physics (which explains the macroscopic) and explores light-matter interaction in macroscopic quantum physics.
“Levitated optomechanical systems provide a clean platform for studying quantum optics, information science, and precision measurement and sensing,” said Bhattacharya, an associate professor in RIT’s School of Physics and Astronomy and a member of the Future Photon Initiative.
To explore different nanosystems for the Office of Naval Research, Bhattacharya isolates a nanodiamond in a pocket of light. Suspension in laser light turns the particle into a floating probe. Bhattacharya is interested in the signatures carried in the light and the information it reveals about the electromagnetic fields and the gravitational forces surrounding the nanoparticle.
He collaborates with postdoctoral associate Pardeep Kumar and RIT undergraduate physics major Wyatt Wetzel. This summer, a visiting undergraduate from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Peter Mizes, joined his Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics Theory Group. Bhattacharya tests his theoretical predictions in a lab run by his collaborator Nick Vamivakas, an experimental physicist at the University of Rochester’s Institute of Optics.
His first study for the Office of Naval Research determined the smallest force that could be detected with a diamond crystal that levitated without spinning. The new project investigates the outcomes of three nanosystems, each using nanoparticles optically trapped under different conditions:
· A particle containing an impurity which acts as a spin sensitive to magnetic fields or as an excess charge sensitive to electric fields;
· A particle moving like a pendulum in three dimensions;
· A particle larger than the wavelength of light entrapping it.
Quantum mechanics is a door to a world on the nanoscale and is governed by a different set of physical laws.
“Unique rules apply in quantum physics,” Bhattacharya said. “It is not the day-to-day physical universe familiar to our experience.”
Optomechanics explores interactions between light and tiny particles of matter within the nano-realm. Sensing technology advanced at these submicroscopic scale promises finer measurements of physical properties that describe the world, such as electric and magnetic fields, temperature, force, velocity, acceleration, gravitation.
According to Bhattacharya, quantum sensors might someday detect gravitational waves, find dark matter, perfect quantum computing and create precise accelerometers—the technology that rights display screens held at any angle.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Susan Gawlowicz
Rochester Institute of Technology
University News Services
@SGawlowicz
585-475-5061
Copyright © Rochester Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








