Home > Press > Metal nanoparticles induced visible-light photocatalysis: Mechanisms, applications, ways of promoting catalytic activity and outlook
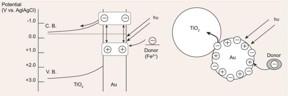 |
| Proposed mechanism for the photoelectrochemistry: charges are separated at a visible-light-irradiated Au NPs TiO2 system. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
In the quest to solve solar energy conversion as well as environmental remediation issues, photocatalysis using sunlight have been attracting tremendous attention. Various semiconductors with large band gaps have been proven to be effective under UV light, e.g., TiO2. However, UV light accounts for only ~4% while visible light occupies ~43% of total sunlight. From the perspective of both chemistry and practical applications, it is undoubtedly important to develop visible-light-responsive photocatalytic materials.
Metal nanoparticles induced visible-light photocatalysis: Mechanisms, applications, ways of promoting catalytic activity and outlook
Beijing, China | Posted on April 27th, 2017Over the past several years, coinage metal (Au, Ag and Cu) nanoparticles (NPs) photosensitization over semiconductors with a large band gap has emerged as a promising strategy for developing visible-light responsive photocatalytic materials. In this review, mechanisms of metal-induced photocatalysis (MIP) were first summarized, e.g., hot-electron transfer (see in the Figure 1). Subsequently, the progress towards MIP applications in photocatalytic and PEC water splitting, photoreduction of CO2 and activation of inert molecules such as CH4, N2 were reviewed. Generally, visible-light activity or enhancement was achieved after the introduction of these metal NPs. Nevertheless, for most present metal induced photocatalytic water-splitting under visible light, the obtained apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) was relatively low (i.e. <1%). So, developing efficient metal semiconductor composite (MSC) materials is still highly needed in this field. To highlight this point, the authors summarized important works in promoting the efficiency of MIP from perspective of achieving broadband or effective light-harvesting, enhancing charge-carrier separation, decoration with cocatalyst etc.
On the other hand, it is undoubted that particle-size effect was important even crucial in MIP systems. Particular attention was paid on this issue and selected works were reviewed though consensus has not been reached yet. Some researchers claimed that larger metal NPs were favorable for its strong SPR intensity leading to high electron transfer efficiency, while some others pointed out that smaller ones were better because of more efficient charge separation could be achieved. Compromise viewpoint also existed, i.e., both small and large metal NPs were important. So, more effort is needed on this issue.
Exploring light absorption of metal NPs in photocatalysis represents a class of novel and promising approaches in exploring efficient visible-light responsive photocatalysts. However, to achieve this goal, there are still many challenges to be addressed. At the end of this review, the authors briefly discussed the challenges and possible development directions of MIP. It includes deeper understanding the mechanism behind MIP, further improve the efficiency, rational design and precise control of plasmonic metal etc. For detailed information, please refer to the article "Metal nanoparticles induced photocatalysis", https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwx019 .
###
This research received funding from the National Basic Research Program of China and the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China.
####
About Science China Press
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lequan Liu
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








