Home > Press > NUS engineers develop low-cost, flexible terahertz radiation source for fast, non-invasive screening: Novel invention presents promising applications in spectroscopy, safety surveillance, cancer diagnosis, imaging and communication
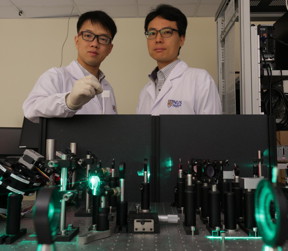 |
| This is the team's low-cost THz radiation sources, which can be powered by a low-power laser, present promising applications in spectroscopy, safety surveillance, cancer diagnosis, imaging and communication. CREDIT National University of Singapore |
Abstract:
Portable handheld sensors for detecting explosives, wearable sensors that can detect chemical agents, compact devices for fast and accurate identification of defects in computing chips as well as advanced, non-invasive imaging techniques that could detect tiny tumours could become a reality sooner than expected as researchers around the world are actively studying novel ways to exploit terahertz (THz) technology. Giving a big boost to this global research effort is a major technological breakthrough in terahertz technology achieved by researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS).
NUS engineers develop low-cost, flexible terahertz radiation source for fast, non-invasive screening: Novel invention presents promising applications in spectroscopy, safety surveillance, cancer diagnosis, imaging and communication
Singapore | Posted on February 1st, 2017Led by Associate Professor Yang Hyunsoo and Dr Wu Yang from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the NUS Faculty of Engineering and NUS Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Institute, the research team has successfully developed high performance and low-power driven THz emitters that could be mass-produced at low cost, addressing a critical challenge for industrial application of THz technology. These THz emitters, which are used for the generation of THz waves, can also function on flexible surfaces without compromising on performance.
The research team published the findings of their study in the scientific journal Advanced Materials on 25 January 2017. This invention was achieved in collaboration with researchers from the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering under Singapore's Agency for Science, Technology and Research, as well as Tongji University in China.
"Our invention is a big step forward in THz technology and we believe that this will greatly accelerate its application in various fields. For instance, in the area of safety surveillance, our invention can contribute towards miniaturisation of bulky THz systems to be used in the detection of dangerous chemicals and explosives for protection against hostile threats. Affordable and high performance THz screening devices could also improve disease diagnosis and benefit patients. Furthermore, fabricating our device on a flexible surface also opens up many exciting possibilities for it to be incorporated into wearable devices," explained Assoc Prof Yang.
Making waves in terahertz
THz waves have attracted a lot of attention in the past two decades as they have promising applications in a wide range of areas from medicine, surveillance to computing and communication. THz waves, which have wavelengths ranging from tens of microns to a few millimetres, occupy the space between microwaves and infrared light waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Being non-ionising as well as non-destructive, THz waves can pass through non-conducting materials such as clothes, paper, wood and brick, making them ideal for applications in areas such as cancer diagnosis, detection of chemicals, drugs and explosives, coating analysis and quality control of integrated circuit chips. However, current THz sources are large, multi-component systems that are heavy and expensive. Such systems are also hard to transport, operate, and maintain.
Hence, the flexible, low-cost THz radiation sources developed by the research team potentially paves the way for greater adoption of THz technology and contribute towards the commercialisation of a wide range of THz applications.
Low-cost, flexible and low-power driven THz emitters
"Traditional methods of generating THz waves, such as through the exciting of electro-optical crystals or photoconductive antennas, often require expensive and bulky high power lasers or extremely expensive and sophisticated device fabrication processes. Our team's THz emitters have displayed better performance compared to existing devices in many aspects. At the same time, we have also developed a fabrication process to produce these novel THz emitters in large quantities at a low cost," said Dr Wu, who is the first author of the study.
Developed using metallic thin film heterostructures that are 12-nanometre in thickness, the novel radiation sources emit broadband THz waves with a higher power output than a standard 500-micrometre thick rigid electro-optical crystal emitter. In addition, the novel emitters can be powered by a low-power laser, hence lowering the operating cost substantially.
The research team also devised a novel, low-cost fabrication technique to produce the emitters. A large wafer-scale film can be deposited and subsequently diced to a large quantity of ready-to-use devices, thus making this production method commercially scalable. The research team also tested their device on flexible surfaces and found that its performance was not compromised despite being subjected to a large bending curvature.
Moving forward, the team plans to build a compact spectroscopy system using THz technology based on its advanced THz emitters. The researchers are also looking into enhancing THz emission for specific wavelengths, which will be beneficial for a wide range of THz-related studies and applications. The research team has filed a patent for the invention and hopes to work with industry partners to further explore various applications of this novel technology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Goh Yu Chong
65-660-11653
Copyright © National University of Singapore
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








