Home > Press > Self-healable battery Lithium ion battery for electronic textiles grows back together after breaking
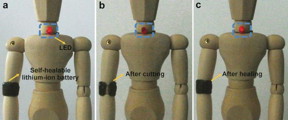 |
| Battery, heal thyself: a new family of solid-state flexible aqueous lithium-ion batteries that can self-heal has been created using aligned carbon nanotube sheets loaded with LiMn2O4 and LiTi2(PO4)3 nanoparticles on a polymer substrate as electrodes and Li2SO4/carboxymethylcellulose as gel electrolyte and separator. The battery performance was well maintained after repeated cycles of cutting and self-healing. CREDIT (C) Wiley-VCH 2016 |
Abstract:
Electronics that can be embedded in clothing are a growing trend. However, power sources remain a problem. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, scientists have now introduced thin, flexible, lithium ion batteries with self-healing properties that can be safely worn on the body. Even after completely breaking apart, the battery can grow back together without significant impact on its electrochemical properties.
Self-healable battery Lithium ion battery for electronic textiles grows back together after breaking
Hoboken, NJ | Posted on October 20th, 2016Existing lithium ion batteries for wearable electronics can be bent and rolled up without any problems, but can break when they are twisted too far or accidentally stepped on--which can happen often when being worn. This damage not only causes the battery to fail, it can also cause a safety problem: Flammable, toxic, or corrosive gases or liquids may leak out.
A team led by Yonggang Wang and Huisheng Peng has now developed a new family of lithium ion batteries that can overcome such accidents thanks to their amazing self-healing powers. In order for a complicated object like a battery to be made self-healing, all of its individual components must also be self-healing. The scientists from Fudan University (Shanghai, China), the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (South Korea), and the Samsung R&D Institute China, have now been able to accomplish this.
The electrodes in these batteries consist of layers of parallel carbon nanotubes. Between the layers, the scientists embedded the necessary lithium compounds in nanoparticle form (LiMn(2)O(4) for one electrode, LiTi(2)(PO(4))(3) for the other). In contrast to conventional lithium ion batteries, the lithium compounds cannot leak out of the electrodes, either while in use or after a break. The thin layer electrodes are each fixed on a substrate of self-healing polymer. Between the electrodes is a novel, solvent-free electrolyte made from a cellulose-based gel with an aqueous lithium sulfate solution embedded in it. This gel electrolyte also serves as a separation layer between the electrodes.
After a break, it is only necessary to press the broken ends together for a few seconds for them to grow back together. Both the self-healing polymer and the carbon nanotubes "stick" back together perfectly. The parallel arrangement of the nanotubes allows them to come together much better than layers of disordered carbon nanotubes. The electrolyte also poses no problems. Whereas conventional electrolytes decompose immediately upon exposure to air, the new gel is stable. Free of organic solvents, it is neither flammable nor toxic, making it safe for this application.
The capacity and charging/discharging properties of a battery "armband" placed around a doll's elbow were maintained, even after repeated break/self-healing cycles.
###
About the Author
Dr. Huisheng Peng is Changjiang Chair Professor at Fudan University with an appointment in area of polymer science. His work centers on the development of novel fiber-shaped energy harevesting and storage devices.
www.polymer.fudan.edu.cn/polymer/research/Penghs/main.htm
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mario Mueller
Copyright © Wiley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wearable electronics
![]() Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








