Home > Press > Study finds surface texture of gallium nitride affects cell behavior
 |
Abstract:
“Nanoscale topography, semiconductor polarity and surface functionalization: additive and cooperative effects on PC12 cell behavior”
Authors: Patrick J. Snyder, Ramon Collazo and Albena Ivanisevic, North Carolina State University; Ronny Kirste, North Carolina State University and Adroit Materials
Published: Oct. 10, RSC Advances
DOI: 10.1039/C6RA21936E
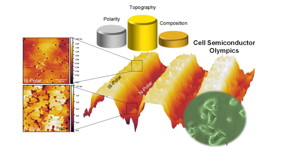
Abstract: This work compares the behavior of PC12 cells on planar and patterned III-nitride materials with nanostructured topographies. Three different materials’ compositions containing N-polar and Ga-polar areas are studied: Al0.8Ga0.2N, Al0.7Ga0.3N, and GaN. Surface microscopy and spectroscopy, along with biological assays are used to understand the connection between nanoscopic features, polarity and surface functionalization. All materials are modified using a solution based approach to change their surface composition. The results demonstrate that altering the surface hydrophobicity can be used to generate additive effects with respect to protein adsorption in addition to the cooperative effects observed with respect to planes’ polarity and topography. The work also details differences in the release of metal ions from clean and functionalized nanostructured III-polar and N-polar semiconductors in cell culture media, and their relationship to changes in cell response through quantification of cell viability and the production of reactive oxygen species. Our results demonstrate that nanoscale topography can be linked to additional parameters at the cell-semiconductor interface in order to understand and modulate PC12 cell behavior.
Study finds surface texture of gallium nitride affects cell behavior
Raleigh, NC | Posted on October 17th, 2016Researchers at North Carolina State University have determined that the surface texture of gallium nitride (GaN) materials can influence the health of nearby cells. The work is significant because GaN is a material of interest for developing new devices that can control cellular behavior.
GaN materials have a unique suite of properties that make them viable candidates for bioelectronic devices: you can tune the charge on the surface of the materials; the materials don't easily degrade in aqueous environments like the body; and they are nontoxic.
"But while living cells will survive in the presence of GaN, we wanted to know if we could influence the behavior of the cells by changing the make-up of the GaN material," says Patrick Snyder, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper on the work. "Basically, we wanted to know if engineering the GaN could influence the health and metabolism of the surrounding cells."
To do this, the researchers tested three different materials: GaN, and two variations of aluminum gallium nitride - Al0.8Ga0.2N and Al0.7Ga0.3N. The researchers manipulated the surface of the materials, creating rough and smooth versions of each. Lastly, the researchers modified the surface chemistry of the materials to make them more or less attractive to water - hydrophilic or hydrophobic, respectively.
For example, there were six types of GaN material: hydrophobic, hydrophilic and unmodified rough GaN; and hydrophobic, hydrophilic and unmodified smooth GaN. The same was also true for both compositions of AlGaN.
The researchers then used the various GaN materials as substrates for growing PC12 cells - a line of well-studied model cells that are well understood.
During the seven-day experiment, the researchers monitored the cell cultures to track the health and metabolism of the cells.
"We found that the roughly-textured AlGaN compositions released more gallium into the cellular environment," Snyder says. "While this did not kill the cells, it did cause metabolic changes."
"This tells us that the topography of the material matters, and can influence cellular behavior," says Albena Ivanisevic, a professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and co-author of the paper. "The work demonstrates that surface textures of bulk materials - like those used to create devices - can have similar effects to what we've previously seen in nanoscale materials."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Safety-Nanoparticles/Risk management
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








