Home > Press > Long may you wave, borophene: Rice University researchers say 2-D boron may be best for flexible electronics
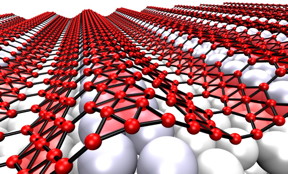 |
| When grown on silver, the two-dimensional form of boron, which is called borophene, takes on corrugations, helped by atomic vacancies in the lattice that make it more flexible. The metallic material may be suitable for use in stretchable, bendable electronics. Credit: Zhuhua Zhang/Rice University |
Abstract:
Though they're touted as ideal for electronics, two-dimensional materials like graphene may be too flat and hard to stretch to serve in flexible, wearable devices. "Wavy" borophene might be better, according to Rice University scientists.
Long may you wave, borophene: Rice University researchers say 2-D boron may be best for flexible electronics
Houston, TX | Posted on October 4th, 2016The Rice lab of theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson and experimental collaborators observed examples of naturally undulating, metallic borophene, an atom-thick layer of boron, and suggested that transferring it onto an elastic surface would preserve the material's stretchability along with its useful electronic properties.
Highly conductive graphene has promise for flexible electronics, Yakobson said, but it is too stiff for devices that also need to stretch, compress or even twist. But borophene deposited on a silver substrate develops nanoscale corrugations. Weakly bound to the silver, it could be moved to a flexible surface for use.
The research appears this month in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
Rice collaborated with experimentalists at Argonne National Laboratory and Northwestern University to study borophene, which has been made in small quantities. Under the microscope, borophene displays corrugations that demonstrate its wavy nature, meaning it can be highly stretched once removed from the substrate, or reattached to a soft one, Yakobson said.
The Rice group builds computer simulations to analyze the properties of materials from the atoms up. Simulations by first author Zhuhua Zhang, a postdoctoral researcher in Yakobson's group, showed that hexagonal vacancies in borophene help soften the material to facilitate its corrugated form.
"Borophene is metallic in its typical state, with strong electron-phonon coupling to support possible superconductivity, and a rich band structure that contains Dirac cones, as in graphene," Yakobson said.
There is a hitch: Borophene needs the underlying structure to make it wavy. When grown on a featureless surface, its natural form resembles graphene, the flat, chicken-wire arrays of carbon atoms. Zhang said borophene is better seen as a triangular lattice with periodic arrays of hexagonal vacancies.
Borophene prefers to be flat because that's where its energy is lowest, Yakobson said. But surprisingly, when grown on silver, borophene adopts its accordion-like form while silver reconstructs itself to match. The corrugation can be retained by "re-gluing" boron onto another substrate.
"This wavy conformation so far seems unique due to the exceptional structural flexibility and particular interactions of borophene with silver, and may be initially triggered by a slight compression in the layer when a bit too many boron atoms get onto the surface," Zhang said.
Co-authors of the paper are Rice alumnus Zhili Hu, Andrew Jacob Mannix and Brian Kiraly of Argonne National Laboratory and Northwestern; Nathan Guisinger of Argonne National Laboratory and Mark Hersam of Northwestern.
The Department of Energy, the Office of Naval Research and the National Science Foundation (NSF) supported the research. The researchers utilized the XSEDE and NSF-supported DAVinCI supercomputer, both administered by Rice’s Center for Research Computing and procured in a partnership with Rice’s Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Flexible Electronics
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








