Home > Press > A 'smart dress' for oil-degrading bacteria
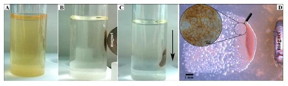 |
| (a,b) Targeted movement of magnetic cells was facilitated by external magnetic field (in liquid media); (c) sedimentation of magnetically concentrated cells; (d) targeted movement and growth of magnetic cells on solid surface (inset shows a higher-magnification view of cells arranged on the surface). CREDIT: From the research article. |
Abstract:
Bionanotechnology research is targeted on functional structures synergistically combining macromolecules, cells, or multicellular assemblies with a wide range of nanomaterials. Providing micrometer-sized cells with tiny nanodevices expands the uses of the cultured microorganisms and requires nanoassembly on individual live cells.
A 'smart dress' for oil-degrading bacteria
Kazan, Russia Federation | Posted on July 24th, 2016Surface engineering functionalizes the cell walls with polymer layers and/or nanosized particles and has been widely employed to modify the intrinsic properties of microbial cells. Cell encapsulation allows fabricating live microbial cells with magnetic nanoparticles onto cell walls, which mimics natural magnetotactic bacteria.
For this study researchers from Kazan Federal University and Louisiana Tech University chose Alcanivorax borkumensis marine bacteria as a target microorganism for cell surface engineering with magnetic nanoparticles for the following reasons: (1) these hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria are regarded as an important tool in marine oil spill remediation and potentially can be used in industrial oil-processing bioreactors, therefore the external magnetic manipulations with these cells seems to be practically relevant; (2) A. borkumensis are marine Gram-negative species having relatively fragile and thin cell walls, which makes cell wall engineering of these bacteria particularly challenging.
Rendering oil-degrading bacteria with artificially added magnetic functionality is important to attenuate their properties and to expand their practical use.
Cell surface engineering was performed using polycation-coated magnetic nanoparticles, which is a fast and straightforward process utilizing the direct deposition of positively charged iron oxide nanoparticles onto microbial cells during a brief incubation in excessive concentrations of nanoparticles. Gram-negative bacteria cell walls are built from the thin peptidoglycan layer sandwiched between the outer membrane and inner plasma membrane, with lipopolysaccharides rendering the overall negative cell charge, therefore cationic particles will attach to the cell walls due to electrostatic interactions.
Rod-like 0.5-μm diameter Gram-negative bacteria A. borkumensis were coated with 70?100 nm magnetite shells. The deposition of nanoparticles was performed with extreme care to ensure the survival of magnetized cells.
The development of biofilms on hydrophobic surface is a very important feature of A. borkumensis cells because this is how these cells attach to the oil droplets in natural environments. Consequently, any cell surface modification should not reduce their ability to attach and proliferate as biofilms. Here, at all concentrations of PAH- magnetite nanoparticles investigated, authors of the study detected the similar biofilm growth patterns. Overall, the magnetized cells were able to proliferate and exhibited normal physiological activity.
The next generations of the bacteria have a tendency to remove the artificial shell returning to the native form. Such magnetic nanoencapsulation may be used for the A. borkumensis transportation in the bioreactors to enhance the spill oil decomposition at certain locations.
###
This study was supported by Russian Science Foundation Grant No. 14-14-00924.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yevgeniya Litvinova
7-843-233-7345
Copyright © Kazan Federal University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








