Home > Press > Yale researchers’ technology turns wasted heat into power
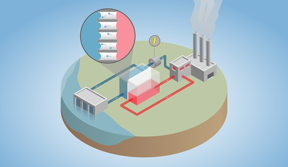 |
| The temperature difference between a waste heat source and the environment drives water across the nanobubble membrane (enlarged) and through a turbine to generate electricity.
Credit: Yale University |
Abstract:
Researchers at Yale have developed a new technology that could make energy from the low-temperature wasted heat produced by industrial sources and power plants, tapping into a widely available — and mostly unused — resource.
Yale researchers’ technology turns wasted heat into power
New Haven, CT | Posted on June 27th, 2016It is estimated that recoverable waste heat in the U.S. alone could power tens of millions of homes. Although existing technologies can reuse high-temperature heat or convert it to electricity, it is difficult to efficiently extract energy from low-temperature heat waste due to the small temperature difference between the plant’s heat discharge and the surrounding environment. Additionally, conventional systems are designed to target a specific temperature difference, so they’re less effective when there are fluctuations in the output of waste heat.
Researchers at Yale’s Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering have developed a new technology that overcomes these challenges. The key is a “nanobubble membrane” that traps tiny air bubbles within its pores when immersed in water. Heating one side of the membrane causes water to evaporate, travel across the air gap, and condense on the opposite side of the membrane. This temperature-driven flow of water across the membrane is then directed to a turbine to generate electricity.
To prove the concept, the team built a small-scale system and demonstrated that the nanobubble membranes could produce pressurized flows of water and generate power even with heat fluctuations and temperature differences as small as 20 degrees Celsius — making it feasible for use with the wasted heat from industrial sources. The findings were published online June 27 in the journal Nature Energy.
The researchers used nanostructured membranes with a surface chemistry that helps trap the air bubbles, keeping bubbles contained within pores even when large pressures are generated. These membranes, approximately as thick as two sheets of paper, were made from highly hydrophobic (water-repelling) polymer nanofibers.
“It was critical to identify robust air-trapping membranes that facilitate pressure generation,” said Menachem Elimelech, corresponding author on the paper and the Roberto C. Goizueta Professor of Chemical and Environmental Engineering at Yale. “Without the right membrane, water would displace the air in the pores, and the process would not be feasible.”
The demonstration of the prototype convinced the researchers of the value of the technology.
“We found that the efficiency of this system can exceed that of comparable technologies,” said Anthony Straub, first author on the study and a doctoral student in chemical and environmental engineering. “The process also only uses water, so it is cost-effective and environmentally friendly.”
The researchers plan to continue work on the technology, developing improved membranes that can better trap air bubbles. They also are investigating how large-scale future systems will perform.
In addition to Elimelech and Straub, the research team included Ngai Yin Yip, a former doctoral student at Yale and current assistant professor at Columbia University; Shihong Lin, a former Yale postdoc and current assistant professor at Vanderbilt University; and Jongho Lee, a postdoc in chemical and environmental engineering at Yale.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
William Weir
203-317-9267
Copyright © Yale University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Industrial
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








