Home > Press > The next generation of carbon monoxide nanosensors
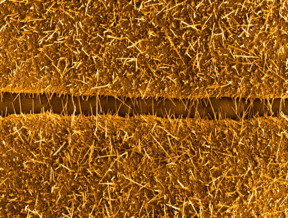 |
| This is an adaptation of a scanning electron microscopy image of copper oxide nanowires bridging the gap between neighbouring copper microstructures CREDIT: OIST |
Abstract:
The detection of carbon monoxide (CO) in the air is a vital issue, as CO is a poisonous gas and an environmental pollutant. CO typically derives from the incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels, such as cooking gas and gasoline; it has no odour, taste, or colour and hence it is difficult to detect. Scientists have been investigating sensors that can determine CO concentration, and a team from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), in tandem with the University of Toulouse, has found an innovative method to build such sensors.
The next generation of carbon monoxide nanosensors
Okinawa, Japan | Posted on May 26th, 2016As a tool for CO detection, scientists use extremely small wires: copper oxide nanowires. Copper oxide nanowires chemically react with CO, creating an electrical signal that can be used to quantify CO concentration. These nanowires are so thin that it is possible to fit more than 1.000 of them in the average thickness of a human hair.
Two issues have hampered the use of nanowires. "The first problem is the integration of nanowires into devices that are big enough to be handled and that can also be easily mass produced," said Prof Mukhles Sowwan, director of the Nanoparticles by Design Unit at OIST. "The second issue is the ability to control the number and position of nanowires in such devices." Both these difficulties might have been solved by Dr Stephan Steinhauer, postdoctoral scholar at OIST, together with Prof Sowwan, and researchers from the University of Toulouse. They recently published their research in the journal ACS Sensors.
"To create copper oxide nanowires, you need to heat neighbouring copper microstructures. Starting from the microstructures, the nanowires grow and bridge the gap between the microstructures, forming an electrical connection between them," Dr Steinhauer explained. "We integrated copper microstructures on a micro-hotplate, developed by the University of Toulouse. A micro-hotplate is a thin membrane that can heat up to several hundred Celsius degrees, but with very low power consumption." Thanks to the micro-hotplate, researchers have a high degree of control over the quantity and position of the nanowires. Also, the micro-hotplate provides scientists with data on the electrical signal that goes through the nanowires.
The final result is an exceptionally sensitive device, capable of detecting very low concentrations of CO. "Potentially, miniaturized CO sensors that integrate copper oxide nanowires with micro-hotplates are the first step towards the next generation of gas sensors," Prof Sowwan commented. "In contrast to other techniques, our approach is cost effective and suitable for mass production."
This new method could also help scientists in better understanding the sensor lifetime. The performance of a sensor decreases overtime, and this is a major issue in gas sensing. Data obtained with this method could help scientists in understanding the mechanisms behind such phenomenon, providing them with information that starts at the very beginning of the sensor lifetime. Traditionally, researchers first grow the nanowires, then connect the nanowires to a device, and finally start measuring the CO concentration. "Our method allows to grow the nanowires in a controlled atmosphere, where you can immediately perform gas sensing measurements," Dr Steinhauer noted. "Basically, you stop growing and start measuring, all in the same location."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kaoru Natori
81-989-662-389
Copyright © Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








