Home > Press > Scientists have put a high precision blood assay into a simple test strip: Researchers have developed a new biosensor test system based on magnetic nanoparticles
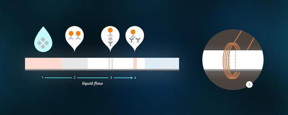 |
| A droplet of the test liquid is applied to the strip (1). The liquid, which spreads along the strip due to capillary action, captures magnetic particles that are "linked" with antibodies to the test protein (2). As they move along the strip, the particles bind to the required protein. The liquid then meets two lines -- the test line (3) and the control line (4). The test line contains antibodies that capture the protein and also the magnetic markers that were bound to it. The control line is activated in any case if the test strip is suitable for use.
Image courtesy of MIPT Press Service. |
Abstract:
Researchers from the General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (GPI RAS) and Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) have developed a new biosensor test system based on magnetic nanoparticles. It is designed to provide highly accurate measurements of the concentration of protein molecules (e.g. markers, which indicate the onset or development of a disease) in various samples, including opaque solutions or strongly coloured liquids.
Scientists have put a high precision blood assay into a simple test strip: Researchers have developed a new biosensor test system based on magnetic nanoparticles
Moscow, Russia | Posted on February 3rd, 2016The new development is similar (in its principal) to a pregnancy test. The analysis is conducted using small test strips made of porous material with two test lines. A droplet of the sample liquid is applied to one end of the strip and after a short period the result is shown as the activation of one or both lines. These test strips can be stored for a long time before being used. The test can be done quickly and does not need to be carried out by specially trained staff; tests can easily be performed next to a patient or even in field conditions.
At molecular level, the magnetic nanoparticles "link" with antibodies to the required protein and then they are placed on a porous plate close to the intended point of contact with the test solution. The liquid, which spreads along the plate due to capillary action, captures the magnetic particles. It then meets two lines - the test line and the control line. The test line contains antibodies that capture the protein in question and also the magnetic markers that became attached to molecules of the protein due to the fact that the nanoparticles are also "linked" to the antibodies. The control line only captures the antibodies with magnetic markers, and it will be activated in any case, if the test strip is usable. The control line serves as an indicator as to whether the test is suitable for use, the protein antibodies in it have not been destroyed due to improper storage, and the test liquid has been applied correctly.
After the sample has permeated the test strip and the antibodies have interacted with one another, the result can be read. This is as far as the resemblance to a pregnancy test goes. In a "classic" pregnancy test, the result can either be "yes" or "no". With this test, however, scientists are not only able to, with a high level of sensitivity, detect a protein, but they can also accurately determine the concentration of the protein. The accuracy of determining the concentration will even exceed the accuracy of methods that are only performed in laboratory conditions by trained staff.
Alexey Orlov, the corresponding author of the study and a Research Fellow of GPI RAS (who also completed an undergraduate degree at MIPT in 2010, and a postgraduate degree in 2013): "Normally, tests that can be performed not only under lab conditions but also in the field, use fluorescent or coloured markers and the results are determined visually, by sight or by using a video camera. In our case, we are using magnetic particles, which have a significant advantage: they can be used to conduct analyses even if the test strip is dipped into a completely opaque liquid, to determine the substances in whole blood for example. The precise numerical measurement is conducted entirely electronically using a portable device. This completely excludes any ambiguity."
The scientists note that along with the high level of sensitivity of determining the concentration of a protein, the new test system also allows measurements to be taken over a wide dynamic range: the upper limit of the test concentration is more than 4000 times greater than the lower limit.
Dynamic range is a familiar term in photography: in relation to a camera, it means the ability of the image sensor or film to distinguish gradations of brightness without washing out to white or converting an image into a dark spot. In biochemical measurements, dynamic range implies the ability to measure the concentration of a protein in a very dilute solution as well as in a very saturated solution.
The new system was tested by measuring 0.025 nanograms per millilitre of prostate-specific antigen in the blood (the "healthy" range is anything lower than 4 nanograms). Prostate-specific antigen is one of the most commonly monitored markers in clinical examinations on men.
Prostate-specific antigen, PSA, is one of the possible markers for prostate cancer - and it is also used in forensics to detect traces of semen. Both applications have certain limitations and they are not able to conclusively provide a diagnosis/prove the guilt of a suspect, but the new biosensor platform will be able to do more than analyse PSA; this particular protein was chosen as a demonstration of the method's capabilities.
This level of sensitivity of determining PSA is enough to tell whether there has been a recurrence after the removal of the prostate, and the results obtained give an idea of the potential of the new development. It is not only able to indicate when a particular indicator is outside of the normal range, but it can also be used to easily trace the dynamics of the concentration of protein markers in a disease.
Having checked the results obtained by the new method against the "gold standard" for determining PSA - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the scientists proved that the new test system works well and that it has significant advantages over traditional methods.
In the new test system, the researchers used their own patented method MPQ (magnetic particle quantification) to precisely count magnetic nanoparticles by their nonlinear magnetization. Using this method, scientists are able to record anything above 60 zeptomoles (the prefix zepto- means ten to the minus twenty-first power!) of nanoparticles in a linear range exceeding ten million times. These parameters have never been recorded at this level before. The method involves applying an alternating magnetic field to the nanoparticles at two frequencies and monitoring the induction response at combinatorial frequencies.
Many methods of analysing substances are based on the fact that test objects, whether they are particles or molecules, are affected by an electromagnetic field. At the correct frequency, a sample starts to either actively absorb radiation, or radiate in response. In this case, the scientists used a combination of two frequencies of the magnetic field and monitored the response at the frequency which is their linear combination - this is called the "combinatorial" frequency.
Maxim Nikitin, the Head of MIPT's Laboratory of Nanobiotechnology and a co-author of the study: "We previously demonstrated the high level of sensitivity of this method of detecting magnetic particles in a joint project with US researchers from the University of Chicago. We used our sensors to record magnetic radioactive nanoparticles based on the isotope 59-Fe in the bodies of animals in vivo (see ?. Nikitin et al., J.Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07A304). In particular, it was found that the threshold for detection using this electronic method coincides with the reporting threshold of accompanying gamma radiation, which means that radioactive markers can be replaced with magnetic nanoparticles in a number of various biophysical studies. In the present study, we use this methodology to achieve ultra-sensitivity for conducting immunoassays."
"...the threshold for detection using this electronic method coincides with the reporting threshold of accompanying gamma radiation" means that in a number of biomedical research magnetic markers and the special device to detect them can be used to identify that was previously possible using radioactive preparations. From a doctor's point of view, magnetic products are clearly better for diagnostic studies as they prevent patients from being exposed to excess radiation.
Dr. Petr Nikitin, Head of Research and Head of Laboratory at GPI RAS (graduated from MIPT in 1979): "The magnetic methods developed and the recorders for counting nanomarkers on test strips not only provide these limits and ranges of measurement of concentrations of antigens, but they are also able to effectively control all stages of the process: from the development and optimization of immunoassay protocols to conducting and interpreting results. This, in particular, is achieved by conducting quantitative monitoring of the redistribution of nanomarkers during biochemical reactions along all three-dimensional porous components of test strips, which has not previously been possible using any other method. Furthermore, the iron salts used to synthesize the nanoparticles are comparably more accessible and cheaper than the reagents used to synthesize gold nanoparticles, which are commonly used in threshold tests such as the pregnancy test."
The combination of reliability, accessibility, and high accuracy and sensitivity of the new method means that it is likely to make a rapid transition from a laboratory prototype to mass production. The developers have not yet given a specific timeframe, but they emphasize that their test system can be used not only to diagnose diseases, but also for a number of other applications. The biosensor is able to conduct analyses on food products and medicines; it will also be able to be used to conduct environmental monitoring. And it will be able to do all this at the location itself, without any complicated or expensive equipment.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Valerii Roizen
7-929-992-2721
Copyright © Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
![]() Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere November 17th, 2023
Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere November 17th, 2023
![]() DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on "Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology" May 12th, 2023
DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on "Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology" May 12th, 2023
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








