Home > Press > Stretchy hydrogel 'Band-Aid' senses, lights up, delivers medicine: Water-based 'Band-Aid' senses temperature, lights up, and delivers medicine to the skin
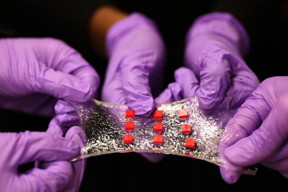 |
| A new stretchy hydrogel can be embedded with various electronics. Here, a sheet of hydrogel is bonded to a matrix of polymer islands (red) that can encapsulate electronic components such as semiconductor chips, LED lights, and temperature sensors.
Credit: Melanie Gonick/MIT |
Abstract:
MIT engineers have designed what may be the Band-Aid of the future: a sticky, stretchy, gel-like material that can incorporate temperature sensors, LED lights, and other electronics, as well as tiny, drug-delivering reservoirs and channels. The "smart wound dressing" releases medicine in response to changes in skin temperature and can be designed to light up if, say, medicine is running low.
Stretchy hydrogel 'Band-Aid' senses, lights up, delivers medicine: Water-based 'Band-Aid' senses temperature, lights up, and delivers medicine to the skin
Cambridge, MA | Posted on December 7th, 2015When the dressing is applied to a highly flexible area, such as the elbow or knee, it stretches with the body, keeping the embedded electronics functional and intact.
The key to the design is a hydrogel matrix designed by Xuanhe Zhao, the Robert N. Noyce Career Development Associate Professor in MIT's Department of Mechanical Engineering. The hydrogel, which Zhao detailed earlier this month, is a rubbery material, mostly composed of water, designed to bond strongly to surfaces such as gold, titanium, aluminum, silicon, glass, and ceramic.
In a new paper published in the journal Advanced Materials, the team reports embedding various electronics within the hydrogel, such as conductive wires, semiconductor chips, LED lights, and temperature sensors. Zhao says electronics coated in hydrogel may be used not just on the surface of the skin but also inside the body, for example as implanted, biocompatible glucose sensors, or even soft, compliant neural probes.
"Electronics are usually hard and dry, but the human body is soft and wet. These two systems have drastically different properties," Zhao says. "If you want to put electronics in close contact with the human body for applications such as health care monitoring and drug delivery, it is highly desirable to make the electronic devices soft and stretchable to fit the environment of the human body. That's the motivation for stretchable hydrogel electronics."
Zhao's co-authors on the paper are graduate students Shaoting Lin, Hyunwoo Yuk, German Alberto Parada, postdoc Teng Zhang, Hyunwoo Koo from Samsung Display, and Cunjiang Yu from the University of Houston.
A strong and stretchy bond
Typical synthetic hydrogels are brittle, barely stretchable, and adhere weakly to other surfaces.
"They're often used as degradable biomaterials at the current stage," Zhao says. "If you want to make an electronic device out of hydrogels, you need to think of long-term stability of the hydrogels and interfaces."
To get around these challenges, his team came up with a design strategy for robust hydrogels, mixing water with a small amount of selected biopolymers to create soft, stretchy materials with a stiffness of 10 to 100 kilopascals -- about the range of human soft tissues. The researchers also devised a method to strongly bond the hydrogel to various nonporous surfaces.
In the new study, the researchers applied their techniques to demonstrate several uses for the hydrogel, including encapsulating a titanium wire to form a transparent, stretchable conductor. In experiments, they stretched the encapsulated wire multiple times and found it maintained constant electrical conductivity.
Zhao also created an array of LED lights embedded in a sheet of hydrogel. When attached to different regions of the body, the array continued working, even when stretched across highly deformable areas such as the knee and elbow.
A versatile matrix
Finally, the group embedded various electronic components within a sheet of hydrogel to create a "smart wound dressing," comprising regularly spaced temperature sensors and tiny drug reservoirs. The researchers also created pathways for drugs to flow through the hydrogel, by either inserting patterned tubes or drilling tiny holes through the matrix. They placed the dressing over various regions of the body and found that even when highly stretched the dressing continued to monitor skin temperature and release drugs according to the sensor readings.
Yuk says an immediate application of the technology may be as a stretchable, on-demand treatment for burns or other skin conditions.
"It's a very versatile matrix," Yuk says. "The unique capability here is, when a sensor senses something different, like an abnormal increase in temperature, the device can on demand release drugs to that specific location and select a specific drug from one of the reservoirs, which can diffuse in the hydrogel matrix for sustained release over time."
Delving deeper, Zhao envisions hydrogel to be an ideal, biocompatible vehicle for delivering electronics inside the body. He is currently exploring hydrogel's potential as a carrier for glucose sensors as well as neural probes. Conventional glucose sensors, implanted in the body, typically spark a foreign-body response from the immune system, which covers the sensors with dense fibers, requiring the sensors to be replaced often. While various hydrogels have been used to coat glucose sensors and prevent such a reaction, the hydrogels are brittle and can detach easily with motion. Zhao says the hydrogel-sensor system his group is developing would likely be robust and effective over long periods. He says a similar case might be made for neural probes.
"The brain is a bowl of Jell-O," Zhao says. "Currently, researchers are trying different soft materials to achieve long-term biocompatibility of neural devices. With collaborators, we are proposing to use robust hydrogel as an ideal material for neural devices, because the hydrogel can be designed to possess similar mechanical and physiological properties as the brain."
###
This research was funded, in part, by the Office of Naval Research, the MIT Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies, and the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Abby Abazorius
617-253-2709
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Hydrogels
![]() Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
![]() The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








