Home > Press > Computing at the speed of light: Utah engineers take big step toward much faster computers
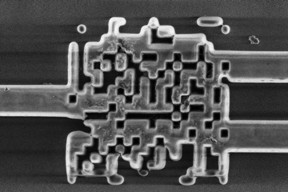 |
| The overhead view of a new beamsplitter for silicon photonics chips that is the size of one-fiftieth the width of a human hair. CREDIT: Dan Hixson/University of Utah College of Engineering |
Abstract:
University of Utah engineers have taken a step forward in creating the next generation of computers and mobile devices capable of speeds millions of times faster than current machines.
Computing at the speed of light: Utah engineers take big step toward much faster computers
Salt Lake City, UT | Posted on May 18th, 2015The Utah engineers have developed an ultracompact beamsplitter -- the smallest on record -- for dividing light waves into two separate channels of information. The device brings researchers closer to producing silicon photonic chips that compute and shuttle data with light instead of electrons. Electrical and computer engineering associate professor Rajesh Menon and colleagues describe their invention today in the journal Nature Photonics.
Silicon photonics could significantly increase the power and speed of machines such as supercomputers, data center servers and the specialized computers that direct autonomous cars and drones with collision detection. Eventually, the technology could reach home computers and mobile devices and improve applications from gaming to video streaming.
"Light is the fastest thing you can use to transmit information," says Menon. "But that information has to be converted to electrons when it comes into your laptop. In that conversion, you're slowing things down. The vision is to do everything in light."
Photons of light carry information over the Internet through fiber-optic networks. But once a data stream reaches a home or office destination, the photons of light must be converted to electrons before a router or computer can handle the information. That bottleneck could be eliminated if the data stream remained as light within computer processors.
"With all light, computing can eventually be millions of times faster," says Menon.
To help do that, the U engineers created a much smaller form of a polarization beamsplitter (which looks somewhat like a barcode) on top of a silicon chip that can split guided incoming light into its two components. Before, such a beamsplitter was over 100 by 100 microns. Thanks to a new algorithm for designing the splitter, Menon's team has shrunk it to 2.4 by 2.4 microns, or one-fiftieth the width of a human hair and close to the limit of what is physically possible.
The beamsplitter would be just one of a multitude of passive devices placed on a silicon chip to direct light waves in different ways. By shrinking them down in size, researchers will be able to cram millions of these devices on a single chip.
Potential advantages go beyond processing speed. The Utah team's design would be cheap to produce because it uses existing fabrication techniques for creating silicon chips. And because photonic chips shuttle photons instead of electrons, mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets built with this technology would consume less power, have longer battery life and generate less heat than existing mobile devices.
The first supercomputers using silicon photonics -- already under development at companies such as Intel and IBM -- will use hybrid processors that remain partly electronic. Menon believes his beamsplitter could be used in those computers in about three years. Data centers that require faster connections between computers also could implement the technology soon, he says.
###
Co-authors on the paper include research associate Randy Polson and doctoral students Bing Shen and Peng Wang.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Vince Horiuchi
801-585-7499
University of Utah College of Engineering
72 S. Central Campus Dr.
Room 1650 WEB
Salt Lake City, UT 84112
801-581-6911
fax: 801-581-8692
http://www.coe.utah.edu
Copyright © University of Utah
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








