Home > Press > Pseudoparticles travel through photoactive material: KIT scientists measure important process in the conversion of light energy -- publication in Nature Communications
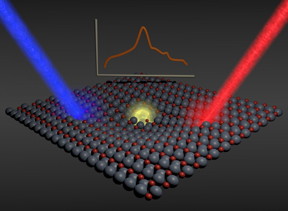 |
| Using the photoactive zinc oxide material, scientists studied the formation and migration of so-called polarons. CREDIT: Figure: Patrick Rinke/Aalto University |
Abstract:
Researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have unveiled an important step in the conversion of light into storable energy: Together with scientists of the Fritz Haber Institute in Berlin and the Aalto University in Helsinki/Finland, they studied the formation of so-called polarons in zinc oxide. The pseudoparticles travel through the photoactive material until they are converted into electrical or chemical energy at an interface. Their findings that are of relevance to photovoltaics among others are now published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Pseudoparticles travel through photoactive material: KIT scientists measure important process in the conversion of light energy -- publication in Nature Communications
Karlsruhe, Germany | Posted on April 24th, 2015Processes converting light into storable energy may contribute decisively to a sustainable energy supply. For billions of years, nature has been using such processes for photosynthesis to form carbohydrates with the help of light. In research, phototcatalysis that uses light to accelerate chemical processes is gaining importance. In the past years, researchers also achieved considerable progress in photovoltaics converting incident sunlight directly into electrical energy. Efficiency constantly improved.
However, the processes underlying photovoltaics have hardly been studied in detail so far. "Conversion of photons, i.e. light particles, into electricity takes several steps," Professor Christof Wöll, Head of the Institute of Functional Interfaces (IFG) of KIT, explains. First, light is absorbed in a photoactive material. Single electrons are removed from their site and leave a hole there. The electron-hole pairs are stable for a short term only. Then, they either decay under the emission of light or are separated into an electron and a hole that move in the material independently of each other. The fate of this charged particle then depends on the material.
In most materials, free holes are not stable, but converted into so-called polarons under energy loss. A polaron is a special pseudoparticle composed of a particle and its interaction with the environment. The polarons formed are stable for a longer term and travel through the photoactive material until they are converted into electrical or chemical energy at an interface.
Researchers of KIT under the direction of Professor Christof Wöll have now carried out experiments using photoactive zinc oxide material in order to study the formation and migration of polarons. They employed a worldwide unique experimental setup for infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) with a temporal resolution of 100 milliseconds and measured infrared spectra of zinc oxide monocrystals and observed intensive absorption bands, i.e. fingerprints, of a so far unknown pseudoparticle. Interpretation of the data and identification of this new particle were big challenges for the KIT scientists. In cooperation with a group working at the Fritz Haber Institute and the Excellence Center for Computational Nanoscience (COMP) of Aalto University, however, they succeeded in unambiguously allocating the absorption bands to so-called hole polarons. "This is an important finding made in 2015, the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies," Professor Wöll says.
###
Hikmet Sezen, Honghui Shang, Fabian Bebensee, Chengwu Yang, Maria Buchholz, Alexei Nefedov, Stefan Heissler, Christian Carbogno, Matthias Scheffler, Patrick Rinke, and Christof Wöll: Evidence for photogenerated intermediate hole polarons in ZnO. Nature Communications, 22nd April 2015. DOI 10.1038/ncomms7901.
####
About Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation pursuing the tasks of a Baden-Wuerttemberg state university and of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. The KIT mission combines the three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation. With about 9,400 employees and 24,500 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Monika Landgraf
49-721-608-47414
Copyright © Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








