Home > Press > Thousands of atoms entangled with a single photon: Result could make atomic clocks more accurate
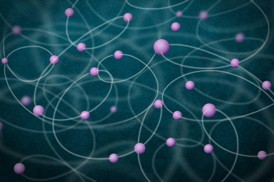 |
| This image illustrates the entanglement of a large number of atoms. The atoms, shown in purple, are shown mutually entangled with one another.
Image: Christine Daniloff/MIT and Jose-Luis Olivares/MIT |
Abstract:
Physicists from MIT and the University of Belgrade have developed a new technique that can successfully entangle 3,000 atoms using only a single photon. The results, published today in the journal Nature, represent the largest number of particles that have ever been mutually entangled experimentally.
Thousands of atoms entangled with a single photon: Result could make atomic clocks more accurate
Cambridge, MA | Posted on March 26th, 2015The researchers say the technique provides a realistic method to generate large ensembles of entangled atoms, which are key components for realizing more-precise atomic clocks.
"You can make the argument that a single photon cannot possibly change the state of 3,000 atoms, but this one photon does -- it builds up correlations that you didn't have before," says Vladan Vuletic, the Lester Wolfe Professor in MIT's Department of Physics, and the paper's senior author. "We have basically opened up a new class of entangled states we can make, but there are many more new classes to be explored."
Vuletic's co-authors on the paper are Robert McConnell, Hao Zhang, and Jiazhong Hu of MIT, as well as Senka Cuk of the University of Belgrade.
Atomic entanglement and timekeeping
Entanglement is a curious phenomenon: As the theory goes, two or more particles may be correlated in such a way that any change to one will simultaneously change the other, no matter how far apart they may be. For instance, if one atom in an entangled pair were somehow made to spin clockwise, the other atom would instantly be known to spin counterclockwise, even though the two may be physically separated by thousands of miles.
The phenomenon of entanglement, which physicist Albert Einstein once famously dismissed as "spooky action at a distance," is described not by the laws of classical physics, but by quantum mechanics, which explains the interactions of particles at the nanoscale. At such minuscule scales, particles such as atoms are known to behave differently from matter at the macroscale.
Scientists have been searching for ways to entangle not just pairs, but large numbers of atoms; such ensembles could be the basis for powerful quantum computers and more-precise atomic clocks. The latter is a motivation for Vuletic's group.
Today's best atomic clocks are based on the natural oscillations within a cloud of trapped atoms. As the atoms oscillate, they act as a pendulum, keeping steady time. A laser beam within the clock, directed through the cloud of atoms, can detect the atoms' vibrations, which ultimately determine the length of a single second.
"Today's clocks are really amazing," Vuletic says. "They would be less than a minute off if they ran since the Big Bang -- that's the stability of the best clocks that exist today. We're hoping to get even further."
The accuracy of atomic clocks improves as more and more atoms oscillate in a cloud. Conventional atomic clocks' precision is proportional to the square root of the number of atoms: For example, a clock with nine times more atoms would only be three times as accurate. If these same atoms were entangled, a clock's precision could be directly proportional to the number of atoms -- in this case, nine times as accurate. The larger the number of entangled particles, then, the better an atomic clock's timekeeping.
Picking up quantum noise
Scientists have so far been able to entangle large groups of atoms, although most attempts have only generated entanglement between pairs in a group. Only one team has successfully entangled 100 atoms -- the largest mutual entanglement to date, and only a small fraction of the whole atomic ensemble.
Now Vuletic and his colleagues have successfully created a mutual entanglement among 3,000 atoms, virtually all the atoms in the ensemble, using very weak laser light -- down to pulses containing a single photon. The weaker the light, the better, Vuletic says, as it is less likely to disrupt the cloud. "The system remains in a relatively clean quantum state," he says.
The researchers first cooled a cloud of atoms, then trapped them in a laser trap, and sent a weak laser pulse through the cloud. They then set up a detector to look for a particular photon within the beam. Vuletic reasoned that if a photon has passed through the atom cloud without event, its polarization, or direction of oscillation, would remain the same. If, however, a photon has interacted with the atoms, its polarization rotates just slightly -- a sign that it was affected by quantum "noise" in the ensemble of spinning atoms, with the noise being the difference in the number of atoms spinning clockwise and counterclockwise.
"Every now and then, we observe an outgoing photon whose electric field oscillates in a direction perpendicular to that of the incoming photons," Vuletic says. "When we detect such a photon, we know that must have been caused by the atomic ensemble, and surprisingly enough, that detection generates a very strongly entangled state of the atoms."
Vuletic and his colleagues are currently using the single-photon detection technique to build a state-of-the-art atomic clock that they hope will overcome what's known as the "standard quantum limit" -- a limit to how accurate measurements can be in quantum systems. Vuletic says the group's current setup may be a step toward developing even more complex entangled states.
"This particular state can improve atomic clocks by a factor of two," Vuletic says. "We're striving toward making even more complicated states that can go further."
This research was supported in part by the National Science Foundation, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Abby Abazorius
617-253-2709
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








