Home > Press > Better batteries inspired by lowly snail shells: Biological molecules can latch onto nanoscale components and lock them into position to make high performing Li-ion battery electrodes, according to new research presented at the 59th annual meeting of the Biophysical Society
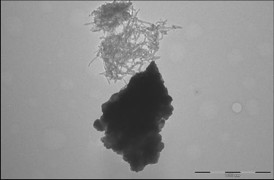 |
| Figure 1a shows lithium manganese nickel oxide and carbon nanotubes clumping separately, with no specific interactions. However, when a multifunctional binding peptide is added to the mixture, as shown in Figure 1b, the peptide binds the dispersed carbon nanotubes to lithium manganese nickel oxide particles. CREDIT: Evgenia Barannikova/UMBC |
Abstract:
Scientists are using biology to improve the properties of lithium ion batteries. Researchers at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) have isolated a peptide, a type of biological molecule, which binds strongly to lithium manganese nickel oxide (LMNO), a material that can be used to make the cathode in high performance batteries. The peptide can latch onto nanosized particles of LMNO and connect them to conductive components of a battery electrode, improving the potential power and stability of the electrode.
Better batteries inspired by lowly snail shells: Biological molecules can latch onto nanoscale components and lock them into position to make high performing Li-ion battery electrodes, according to new research presented at the 59th annual meeting of the Biophysical Society
Washington, DC | Posted on February 12th, 2015The researchers will present their results at the 59th annual meeting of the Biophysical Society, held Feb. 7-11 in Baltimore, Maryland.
"Biology provides several tools for us to solve important problems," said Evgenia Barannikova, a graduate student at UMBC. Barannikova works in the lab of Mark Allen and studies how biological molecules in general can improve the properties of inorganic materials in batteries. "By mimicking biological processes we can find the better solution," she said.
One of the problems currently facing battery researchers is the difficulty of working with nanoscale materials, which due to their extra tiny size can be hard to control and hold in place. The frustrations of working with nanosized materials are worth overcoming, however. Nanostructured electrodes in Li-ion batteries have several advantages over bulk material electrodes, including shorter distances for charge-carrying particles to travel and a high surface area that provides more active sites for electrochemical reactions to occur - all of which translates to batteries that are lighter and longer-lasting.
To take on the challenge of manufacturing on the nanoscale Barannikova and her colleagues have turned for help to biological molecules called peptides. Themselves made up from strings of molecules known as amino acids, peptides are naturally occurring and bind to many different types of organic and inorganic materials, depending on their sequence of the amino acids. They play many roles in the human body, from signaling in the brain to regulating blood sugar, and some drugs, like insulin, are made up of peptides.
One of the inspirations for her research, Barannikova said, was the way that organisms such as mollusks use peptides to control the growth of their shells. They demonstrate remarkable control in order to build intricate nano- and macrostructures from inorganic materials like calcium carbonate, she said.
The researchers borrowed the general approach of the mollusks, but had to employ some lab-bench wizardry to find the appropriate peptide. No snail, after all, makes its shell from lithium manganese nickel oxide.
Barannikova and her colleagues used a procedure called "Phage Display" to screen more than one billion possible peptides in search of one that would stick strongly to lithium manganese nickel oxide. The "peptide library" through which the researchers searched is commercially produced by a laboratory supply company, and contains a vast number of randomly combined amino acid sequences incorporated into a protein made by a virus called the M13 bacteriophage.
The researchers isolated a peptide that binds to lithium manganese nickel oxide by combining the library with a sample of the metal oxide and then repeatedly washing away the peptides that didn't stick to it. The researchers then combined the newly-discovered peptide with a previously isolated peptide that binds to carbon nanotubes. Carbon nanotubes can serve as conductive nanowires in Li-ion electrodes.
The resulting peptide could then form a bridge, binding to both the lithium manganese nickel oxide nanoparticles and the carbon nanotubes and keeping them close to each other so that they can maintain a connection through multiple charging cycles. By helping to maintain a highly organized architecture at the nanoscale, the researchers expect that their peptides will improve the power and cycling stability of future Li-ion batteries, allowing them to be smaller and maintain longer lifetimes.
The team is currently testing how well the new cathodes perform. Going forward, Barannikova plans to make an anode with similar techniques and to integrate the two components. "I hope to demonstrate an entire biotemplated battery in my Ph.D. thesis," she said.
The poster "Solid-binding Peptides as a Biotemplate for Li-ion Battery Electrodes" by Evgenia Barannikova and Mark Allen will be presented from 10:30 a.m. - 12:30 p.m. on Wednesday, February 11, 2015 in Hall C. ABSTRACT: http://tinyurl.com/mkd6p88
###
MORE MEETING INFORMATION
ABOUT THE MEETING
Each year, the Biophysical Society Annual Meeting brings together more than 6,500 researchers working in the multidisciplinary fields representing biophysics. With more than 3,600 poster presentations, over 200 exhibits, and more than 20 symposia, the BPS Annual Meeting is the largest meeting of biophysicists in the world. Despite its size, the meeting retains its small-meeting flavor through its subgroup symposia, platform sessions, social activities and committee programs. The 59th Annual Meeting will be held at the Baltimore Convention Center.
PRESS REGISTRATION
The Biophysical Society invites professional journalists, freelance science writers and public information officers to attend its Annual Meeting free of charge. For press registration, contact Ellen Weiss < > or Jason Bardi at 240-535-4954.
####
About Biophysical Society
The Biophysical Society, founded in 1958, is a professional, scientific Society established to encourage development and dissemination of knowledge in biophysics. The Society promotes growth in this expanding field through its annual meeting, bi-monthly journal, and committee and outreach activities. Its 9,000 members are located throughout the U.S. and the world, where they teach and conduct research in colleges, universities, laboratories, government agencies, and industry.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © Biophysical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Events/Classes
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








