Home > Press > 3-D printing with custom molecules creates low-cost mechanical sensor
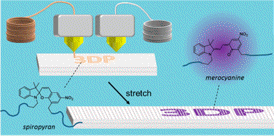 |
| The researchers put slightly different plastics in each of the printer’s two print heads. One of the plastics changes color when it is stretched. A.J. Boydston / UW |
Abstract:
Imagine printing out molecules that can respond to their surroundings. A research project at the University of Washington merges custom chemistry and 3-D printing. Scientists created a bone-shaped plastic tab that turns purple under stretching, offering an easy way to record the force on an object.
3-D printing with custom molecules creates low-cost mechanical sensor
Seattle, WA | Posted on February 10th, 2015"At the UW, this is a marriage that's been waiting to happen - 3-D printing from the engineering side, and functional materials from the chemistry side," said Andrew J. Boydston, a UW assistant professor of chemistry. He is corresponding author on a recent paper in the American Chemical Society's journal of Applied Materials and Interfaces.
Gregory Peterson and Michael Larsen, UW doctoral students in chemistry, created a polymer, or plastic made up of many repeated units strung together, and fed the soft plastic into the UW chemistry lab's commercial 3-D printer.
One print head contained polycaprolactone, similar to what a 3-D printer company sells as Flexible Filament. The other print head contained a plastic that is 99.5 percent identical but the UW team made occasional insertions of a molecule, spiropyran, that changes color when it is stretched.
"We wanted to demonstrate that the functional chemistry could be incorporated readily into already printable materials," Boydston said. "We found that designer chemistry can be incorporated into 3-D printing very rapidly."
The printed tab is a piece of white plastic with barely visible stripes that turn purple under force. It acts as an inexpensive, mechanical sensor with no electronic parts. The whole device took about 15 minutes to print from materials that cost less than a dollar.
The sensor might be used to record force or strain on a building or other structure. Boydston would like to develop a sensor that also records the speed of the force, or impact, which could allow for a football helmet that changes color when hit with sufficient force.
The project is part of a recent collaboration between Boydston's group and co-authors Mark Ganter and Duane Storti, UW mechanical engineers who have developed new 3-D printing materials and techniques.
Different instructions can program the machine to print the plastics in any configuration - with the color-changing part in stripes in the middle, completely encased in the other plastic, or in any other desired shape.
Boydston specializes in organic synthesis, or, in his words: "It means making more complex molecules from simpler, more available ones."
Varying how the plastic is made could yield molecules that respond in different ways.
"Maybe the material isn't currently under stress, but it had been several times prior to your observing it. And so these types of materials could record that load history," Boydston said.
Boydston will continue collaborating with Ganter and Storti, to plan and create more 3-D printed objects that incorporate designer molecules. The 3-D printing technology offers new possibilities, he said, for individualized medical implants or other custom shapes that incorporate engineered molecules that respond to their environment.
"This is definitely an area that we want to continue to expand into," Boydston said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hannah Hickey
206-543-2580
Andrew Boydston
206-616-8195
Copyright © University of Washington
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








