Home > Press > Researchers Make Magnetic Graphene: UC Riverside research could lead to new multi-functional electronic devices
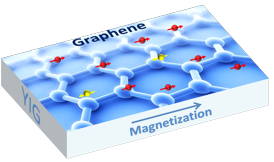 |
| Graphene is a one-atom thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. UC Riverside physicists have found a way to induce magnetism in graphene while also preserving graphene’s electronic properties. IMAGE CREDIT: SHI LAB, UC RIVERSIDE. |
Abstract:
Graphene, a one-atom thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has many desirable properties. Magnetism alas is not one of them. Magnetism can be induced in graphene by doping it with magnetic impurities, but this doping tends to disrupt graphene's electronic properties.
Researchers Make Magnetic Graphene: UC Riverside research could lead to new multi-functional electronic devices
Riverside, CA | Posted on January 27th, 2015Now a team of physicists at the University of California, Riverside has found an ingenious way to induce magnetism in graphene while also preserving graphene's electronic properties. They have accomplished this by bringing a graphene sheet very close to a magnetic insulator - an electrical insulator with magnetic properties.
"This is the first time that graphene has been made magnetic this way," said Jing Shi, a professor of physics and astronomy, whose lab led the research. "The magnetic graphene acquires new electronic properties so that new quantum phenomena can arise. These properties can lead to new electronic devices that are more robust and multi-functional."
The finding has the potential to increase graphene's use in computers, as in computer chips that use electronic spin to store data.
Study results appeared online earlier this month in Physical Review Letters.
The magnetic insulator Shi and his team used was yttrium iron garnet grown by laser molecular beam epitaxy in his lab. The researchers placed a single-layer graphene sheet on an atomically smooth layer of yttrium iron garnet. They found that yttrium iron garnet magnetized the graphene sheet. In other words, graphene simply borrows the magnetic properties from yttrium iron garnet.
Magnetic substances like iron tend to interfere with graphene's electrical conduction. The researchers avoided those substances and chose yttrium iron garnet because they knew it worked as an electric insulator, which meant that it would not disrupt graphene's electrical transport properties. By not doping the graphene sheet but simply placing it on the layer of yttrium iron garnet, they ensured that graphene's excellent electrical transport properties remained unchanged.
In their experiments, Shi and his team exposed the graphene to an external magnetic field. They found that graphene's Hall voltage - a voltage in the perpendicular direction to the current flow - depended linearly on the magnetization of yttrium iron garnet (a phenomenon known as the anomalous Hall effect, seen in magnetic materials like iron and cobalt). This confirmed that their graphene sheet had turned magnetic.
Shi was joined in the study by UC Riverside's Zhiyong Wang (first author of the research paper), Chi Tang, Raymond Sachs and Yafis Barlas.
Grants to Shi and his team members from the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation supported the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Iqbal Pittalwala
Tel: (951) 827-6050
Twitter: UCR_Sciencenews
ADDITIONAL CONTACTS
Jing Shi
Tel: (951) 827-1059
Copyright © UC Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Department of Physics and Astronomy:
Department of Physics and Astronomy:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








