Home > Press > Ki-Bum Lee Patents Technology To Advance Stem Cell Therapeutics
 |
Abstract:
Associate Professor Ki-Bum Lee has developed patent-pending technology that may overcome one of the critical barriers to harnessing the full therapeutic potential of stem cells.
Ki-Bum Lee Patents Technology To Advance Stem Cell Therapeutics
New Brunswick, NJ | Posted on November 13th, 2014One of the major challenges facing researchers interested in regenerating cells and growing new tissue to treat debilitating injuries and diseases such as Parkinson's disease, heart disease, and spinal cord trauma, is creating an easy, effective, and non-toxic methodology to control differentiation into specific cell lineages. Lee and colleagues at Rutgers and Kyoto University in Japan have invented a platform they call NanoScript, an important breakthrough for researchers in the area of gene expression. Gene expression is the way information encoded in a gene is used to direct the assembly of a protein molecule, which is integral to the process of tissue development through stem cell therapeutics.
Stem cells hold great promise for a wide range of medical therapeutics as they have the ability to grow tissue throughout the body. In many tissues, stem cells have an almost limitless ability to divide and replenish other cells, serving as an internal repair system.
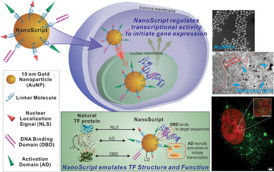
Transcription factor (TF) proteins are master regulators of gene expression. TF proteins play a pivotal role in regulating stem cell differentiation. Although some have tried to make synthetic molecules that perform the functions of natural transcription factors, NanoScript is the first nanomaterial TF protein that can interact with endogenous DNA. ACS Nano, a publication of the American Chemical Society (ACS), has published Lee's research on NanoScript. The research is supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
"Our motivation was to develop a highly robust, efficient nanoparticle-based platform that can regulate gene expression and eventually stem cell differentiation," said Lee, who leads a Rutgers research group primarily focused on developing and integrating nanotechnology with chemical biology to modulate signaling pathways in cancer and stem cells. "Because NanoScript is a functional replica of TF proteins and a tunable gene-regulating platform, it has great potential to do exactly that. The field of stem cell biology now has another platform to regulate differentiation while the field of nanotechnology has demonstrated for the first time that we can regulate gene expression at the transcriptional level."
NanoScript was constructed by tethering functional peptides and small molecules called synthetic transcription factors, which mimic the individual TF domains, onto gold nanoparticles.
"NanoScript localizes within the nucleus and initiates transcription of a reporter plasmid by up to 30-fold," said Sahishnu Patel, Rutgers Chemistry graduate student and co-author of the ACS Nano publication. "NanoScript can effectively transcribe targeted genes on endogenous DNA in a nonviral manner."
Lee said the next step for his research is to study what happens to the gold nanoparticles after NanoScript is utilized, to ensure no toxic effects arise, and to ensure the effectiveness of NanoScript over long periods of time.
"Due to the unique tunable properties of NanoScript, we are highly confident this platform not only will serve as a desirable alternative to conventional gene-regulating methods," Lee said, "but also has direct employment for applications involving gene manipulation such as stem cell differentiation, cancer therapy, and cellular reprogramming. Our research will continue to evaluate the long-term implications for the technology."
Lee, originally from South Korea, joined the Rutgers faculty in 2008 and has earned many honors including the NIH Director's New Innovator Award. Lee received his Ph.D. in Chemistry from Northwestern University where he studied with Professor Chad. A. Mirkin, a pioneer in the coupling of nanotechnology and biomolecules. Lee completed his postdoctoral training at The Scripps Research Institute with Professor Peter G. Schultz. Lee has served as a Visiting Scholar at both Princeton University and UCLA Medical School.
The primary interest of Lee's group is to develop and integrate nanotechnologies and chemical functional genomics to modulate signaling pathways in mammalian cells towards specific cell lineages or behaviors. He has published more than 50 articles and filed for 17 corresponding patents.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Fred Feiner
Yankee Public Relations
(908) 425-4878
Copyright © Rutgers University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








