Home > Press > Blades of grass inspire advance in organic solar cells
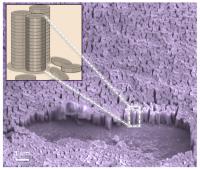 |
| Vertical nanopillars are ideal geometries for getting around the challenges of producing polymer architecture to boost power-conversion efficiency of light to electricity to power electronic devices.
Credit: UMass AMherst |
Abstract:
Using a bio-mimicking analog of one of nature's most efficient light-harvesting structures, blades of grass, a research team has taken a major step in developing long-sought polymer architecture to boost power-conversion efficiency of light to electricity.
Blades of grass inspire advance in organic solar cells
Amherst. MA | Posted on October 2nd, 2014Using a bio-mimicking analog of one of nature's most efficient light-harvesting structures, blades of grass, an international research team led by Alejandro Briseno of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has taken a major step in developing long-sought polymer architecture to boost power-conversion efficiency of light to electricity for use in electronic devices.
Briseno, with colleagues and graduate students at UMass Amherst and others at Stanford University and Dresden University of Technology, Germany, report in the current issue of Nano Letters that by using single-crystalline organic nanopillars, or "nanograss," they found a way to get around dead ends, or discontinuous pathways, that pose a serious drawback when using blended systems known as bulk heterojunction donor-acceptor, or positive-negative (p-n), junctions for harvesting energy in organic solar cells.
Briseno's research group is one of very few in the world to design and grow organic single-crystal p-n junctions. He says, "This work is a major advancement in the field of organic solar cells because we have developed what the field considers the 'Holy Grail' architecture for harvesting light and converting it to electricity." The breakthrough in morphology control should have widespread use in solar cells, batteries and vertical transistors, he adds.
Briseno explains, "For decades scientists and engineers have placed great effort in trying to control the morphology of p-n junction interfaces in organic solar cells. We report here that we have at last developed the ideal architecture composed of organic single-crystal vertical nanopillars." Nanopillars are nanoscale, engineered surfaces with billions of organic posts that resemble blades of grass, and like grass blades they are particularly effective at converting light to energy.
The advance not only addresses the problem of dead ends or discontinuous pathways that make for inefficient energy transfer, but it also solves some instability problems, where the materials in mixed blends of polymers tend to lose their phase-separated behavior over time, degrading energy transfer, the polymer chemist says. Also, materials in blended systems tend to be amorphous to semi-crystalline at best and "this is a disadvantage since charge transport is more efficient in highly crystalline systems."
Specifically, to control the molecular orientation and packing at electrode surfaces, the team combined knowledge about graphene and organic crystals. Though it was difficult, Briseno says, they managed to get the necessary compounds to stack like coins. Stacked compounds are ideal for charge transport since this configuration has the largest charge transport anisotropy. Charge transport anisotropy is a phenomenon where electrons flow faster along a particular crystallographic direction due to close molecule-molecule interactions. In this case, the anisotropy is along the nanopillar, perpendicular to the substrate.
Briseno says, "The biggest challenge in producing this architecture was finding the appropriate substrate that would enable the molecules to stack vertically. We had exploited essentially every substrate possible until we finally succeeded with graphene," he adds, which happened by accident when an undergraduate chose the wrong substrate to grow crystals on.
"For over a week the student was growing vertical crystals and we didn't even realize until we imaged the surface of the substrate with a scanning electron microscope. We were shocked to see little crystals standing upright! We ultimately optimized the conditions and determined the mechanism of crystallization," the polymer chemist adds.
Vertical nanopillars are ideal geometries for getting around these challenges, Briseno says, "because charge separation/collection is most efficient perpendicular to the plastic device. In this case, our nanopillars highly resemble nanograss. Our systems share similar attributes of grass such as high density array system, vertical orientations and the ability to efficiently convert light into energy."
The technique is simple, inexpensive and applicable to a library of donor and acceptor compounds that are commercially available, he notes. "We envision that our nanopillar solar cells will appeal to low-end energy applications such as gadgets, toys, sensors and short lifetime disposable devices."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Janet Lathrop
413-545-0444
Copyright © University of Massachusetts at Amherst
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








