Home > Press > 'Exotic' material is like a switch when super thin
 |
Abstract:
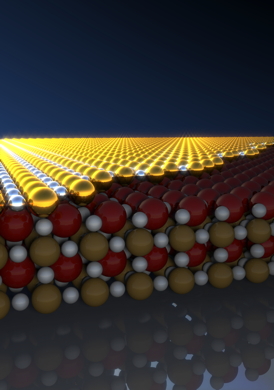
Researchers from Cornell University and Brookhaven National Laboratory have shown how to switch a particular transition metal oxide, a lanthanum nickelate (LaNiO3), from a metal to an insulator by making the material less than a nanometer thick.
'Exotic' material is like a switch when super thin
Ithaca, NY | Posted on April 18th, 2014Ever-shrinking electronic devices could get down to atomic dimensions with the help of transition metal oxides, a class of materials that seems to have it all: superconductivity, magnetoresistance and other exotic properties. These possibilities have scientists excited to understand everything about these materials, and to find new ways to control their properties at the most fundamental levels.
The team of researchers, which published its findings online April 6 in Nature Nanotechnology (to appear in the journal's May issue), includes lead researcher Kyle Shen, associate professor of physics; first author Phil King, a recent Kavli postdoctoral fellow at Cornell now on the faculty at the University of St. Andrews; Darrell Schlom, the Herbert Fisk Johnson Professor of Industrial Chemistry; and co-authors Haofei Wei, Yuefeng Nie, Masaki Uchida, Carolina Adamo, and Shabo Zhu, and Xi He and Ivan Božović.
Using an extremely precise growth technique called molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE), King synthesized atomically thin samples of the lanthanum nickelate and discovered that the material changes abruptly from a metal to an insulator when its thickness is reduced to below 1 nanometer. When that threshold is crossed, its conductivity - the ability for electrons to flow through the material - switches off like a light, a characteristic that could prove useful in nanoscale switches or transistors, Shen said.
Using a one-of-a-kind system at Cornell, which integrates MBE film growth with a technique called angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), King and colleagues mapped out how the motions and interactions of the electrons in the material changed across this threshold, varying the thickness of their oxide films atom by atom. They discovered that when the films were less than 3 nickel atoms thick, the electrons formed an unusual nanoscale order, akin to a checkerboard.
The results demonstrate the ability to control the electronic properties of exotic transition metal oxides at the nanometer scale, as well as revealing the striking cooperative interactions that govern the behavior of the electrons in these ultrathin materials. Their discovery paves the way for making advanced new electronic devices from oxides.
###
The work was supported by the Kavli Institute at Cornell for Nanoscale Science, the Office of Naval Research, the National Science Foundation through the Cornell Center for Materials Research (MRSEC program), and the U.S. Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Syl Kacapyr
607-255-7701
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








