Home > Press > New University of Illinois publication on nanoscale chemical analysis using AFM-IR
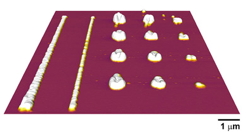 |
| The chemical properties of these polymer nanostructures were measured using AFM-IR from Anasys Instruments. |
Abstract:
Anasys Instruments reports on the recent publication from the University of Illinois which describes the development of a novel technique for chemical identification at the nanometer scale based on AFM-IR. The work is described in a paper published in the Review of Scientific Instruments 84.
New University of Illinois publication on nanoscale chemical analysis using AFM-IR
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on April 30th, 2013For more than 20 years, researchers have been using atomic force microscopy (AFM) to measure and characterize materials at the nanometer scale. However AFM-based measurements of chemistry and chemical properties of materials were generally not possible, until now.
Researchers at the University Illinois report that they have measured the chemical properties of polymer nanostructures as small as 15 nm, using a novel technique called atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR*). The article, "Atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy on 15nm scale polymer nanostructures," appears in the Review of Scientific Instruments 84, published by the American Institute of Physics.
"AFM-IR is a new technique for measuring infrared absorption at the nanometer scale," explained William P. King, an Abel Bliss Professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois. "The first AFM-based measurements could measure the size and shape of nanometer-scale structures. Over the years, researchers improved AFM to measure mechanical properties and electrical properties on the nanometer scale.
"These infrared absorption properties provide information about chemical bonding in a material sample, and these infrared absorption properties can be used to identify the material," added King, who is also the director of the National Science Foundation (NSF) Center for Nanoscale Chemical-Electrical-Mechanical Manufacturing Systems at Illinois. "The polymer nanostructures are about an order of magnitude smaller than those measured previously."
The research is enabled by a new way to analyze the way the nanometer-scale dynamics within the AFM-IR system. The researchers analyzed the AFM-IR dynamics using a wavelet transform, which organizes the AFM-IR signals that vary in both time and in frequency. By separating the time and frequency components, the researchers were able to improve the signal to noise within AFM-IR and to thereby measure significantly smaller samples than previously possible.
The ability to measure the chemical composition of polymer nanostructures is important for a variety of applications, including semiconductors, composite materials, and medical diagnostics. The authors on the research are Jonathan Felts, Hanna Cho, Min-Feng Yu, Lawrence Bergman, Alex Vakakis, and William P. King. The article is available online.
*AFM-IR is a product from Anasys Instruments, Inc.
####
About Anasys Instruments
Anasys Instruments is dedicated to delivering innovative products that measure material properties for samples with spatially varying physical and chemical properties at the nanoscale. Anasys introduced the nano-TA in 2006 which pioneered the field of nanoscale thermal property measurement. In 2010, Anasys introduced the award-winning breakthrough nanoIR™ Platform which pioneered the field of nanoscale IR measurement. Most recently, Anasys is proud to introduce the breakthrough Lorentz Force Contact Resonance, which pioneers the field of wideband nanomechanical spectroscopy.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anasys contact:
Roshan Shetty
Anasys Instruments Corporation
121 Gray Avenue, Suite 100
Santa Barbara
CA 93101 USA
Tel: +1 (805) 730-3310
www.anasysinstruments.com
Media contact:
Jezz Leckenby
Talking Science Limited
39 de Bohun Court
Saffron Walden
Essex CB10 2BA, UK
Tel +44 (0) 1799 521881
Mob +44 (0) 7843 012997
www.talking-science.com
Copyright © Anasys Instruments
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








