Home > Press > Scientists reach the ultimate goal -- controlling chirality in carbon nanotubes
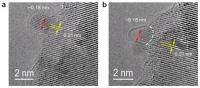 |
| This image shows the initial carbon cap formation on Co nanoparticles.
Credit: Esko Kauppinen |
Abstract:
An ultimate goal in the field of carbon nanotube research is to synthesise single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) with controlled chiralities. Twenty years after the discovery of SWNTs, scientists from Aalto University in Finland, A.M. Prokhorov General Physics Institute RAS in Russia and the Center for Electron Nanoscopy of Technical University of Denmark (DTU) have managed to control chirality in carbon nanotubes during their chemical vapor deposition synthesis.
Scientists reach the ultimate goal -- controlling chirality in carbon nanotubes
Aalto, Finland | Posted on April 29th, 2013Carbon nanotube structure is defined by a pair of integers known as chiral indices (n,m), in other words, chirality.
Chirality defines the optical and electronic properties of carbon nanotubes, so controlling it is a key to exploiting their practical applications, says Professor Esko I. Kauppinen, the leader of the Nanomaterials Group in Aalto University School of Science.
Over the years, substantial progress has been made to develop various structure-controlled synthesis methods. However, precise control over the chiral structure of SWNTs has been largely hindered by a lack of practical means to direct the formation of the metal nanoparticle catalysts and their catalytic dynamics during tube growth.
We achieved an epitaxial formation of Co nanoparticles by reducing a well-developed solid solution in CO, reveals Maoshuai He, a postdoctoral researcher at Aalto University School of Chemical Technology.
For the first time, the new catalyst was employed for selective growth of SWNTs, adds senior staff scientist Hua Jiang from Aalto University School of Science.
By introducing the new catalysts into a conventional CVD reactor, the research team demonstrated preferential growth of semiconducting SWNTs (~90%) with an exceptionally high population of (6,5) tubes (53%) at 500 °C. Furthermore, they also showed a shift of the chiral preference from (6,5) tubes at 500 °C to (7, 6) and (9, 4) nanotubes at 400 °C.
These findings open new perspectives both for structural control of SWNTs and for elucidating their growth mechanisms, thus are important for the fundamental understanding of science behind nanotube growth, comments Professor Juha Lehtonen from Aalto University.
This work is financially supported by the CNB-E project in Aalto University through the Multidisciplinary Institute of Digitalization and Energy (MIDE) program and the Aalto Energy Efficiency program project (MOPPI). This work made use of facilities at Nanomicroscopy Center of Aalto University in Finland and at the Center for Electron Nanoscopy at the Technical University in Denmark sponsored by the A.P. Møller and Chastine Mc-Kinney Møller Foundation.
####
About Aalto University
Aalto University, Finland is a new multidisciplinary science and art community in the fields of science, economics, and art and design. The University is founded on Finnish strengths, and its goal is to develop as a unique entity to become one of the world's top universities. Aalto University's cornerstones are its strengths in education and research. At the new University, there are 20,000 basic degree and graduate students as well as a staff of 5,000 of which 350 are professors.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Esko I. Kauppinen
358-405-098-064
Copyright © Aalto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








