Home > Press > Scientists provide 'new spin' on emerging quantum technologies
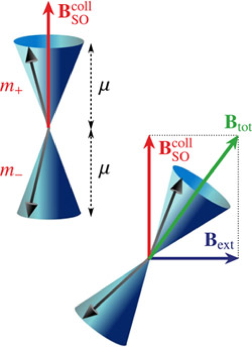 |
| Images illustrate how collective spin excitations behave under the effect of the spin-orbit field, with and without external magnetic field. © 2012 American Physical Society |
Abstract:
An international team of scientists has shed new light on a fundamental area of physics which could have important implications for future electronic devices and the transfer of information at the quantum level.
Scientists provide 'new spin' on emerging quantum technologies
Heslington, UK | Posted on April 23rd, 2013The electrical currents currently used to power electronic devices are generated by a flow of charges. However, emerging quantum technologies such as spin-electronics, make use of both charge and another intrinsic property of electrons - their spin - to transfer and process signals and information.
The experimental and theoretical work, carried out by researchers from York's Department of Physics, the Institute of Nanoscience in Paris and the University of Missouri-Columbia, USA, could have important implications for spintronics and quantum information technologies.
The team looked at semiconductors' structures - the base of current electronic devices and of many spintronic device proposals - and the problems created by internal fields known as spin-orbit fields. In general, these tend to act differently on each electronic spin, causing a phenomenon referred to as 'spin-decoherence'. This means that the electronic spins will behave in a way which cannot be completely controlled or predicted, which has important implications for device functionalities.
To address this problem, the scientists looked at semiconductor structures called 'quantum wells' where the spins can be excited in a collective, coherent way by using lasers and light scattering.
They demonstrated that these collective spin excitations possess a macroscopic spin of quantum nature. In other words, the electrons and their spins act as a single entity making them less susceptible to spin orbit fields, so decoherence is highly suppressed.
The theoretical work was led by Dr Irene D'Amico from York's Department of Physics, and Carsten Ullrich, an Associate Professor from Missouri-Columbia's
Department of Physics. The project began with their prediction about the effect of spin Coulomb drag on collective spin excitations, and developed into a much larger international project spanning over three years, which was funded in the UK by a Royal Society grant, with additional funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
Dr D'Amico said: "This work has developed into a strong international collaboration which has greatly improved our understanding at fundamental level of the role of many-body interactions on the behaviour of electron spins.
"By combining experimental and theoretical work, we were able to demonstrate that through many-body interactions, a macroscopic collection of spins can behave as a single entity with a single macroscopic quantum spin, making this much less susceptible to decoherence. In the future, it may be possible to use these excitations as signals to transport or elaborate information at the quantum level."
After reporting their results in the journal Physical Review Letters last year, the team of scientists confirmed and extended the results by considering different materials and type of excitation. The second set of experiments, were recently reported in Physical Review B (Rapid Communication) and highlighted by the Journal as an 'Editor's Suggestion'.
Dr Florent Perez, who led the experimental work with Florent Baboux, at the CNRS/Université Paris VI, says the results strongly suggest that the quantum nature of the macroscopic spin is universal to collective spin excitations in conductive systems.
He said: "The collaboration with Irene D'Amico and Carsten Ullrich has been particularly powerful to disentangle the puzzle of our data. In our first joint work we constructed an interpretation of the phenomenon which was confirmed in a second investigation carried out on a different system. This paved the way for a universality of the effect."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Caron Lett
44-019-043-22029
Copyright © University of York
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
![]() Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








