Home > Press > Heliatek consolidates its technology leadership by establishing a new world record for organic solar technology with a cell efficiency of 12%
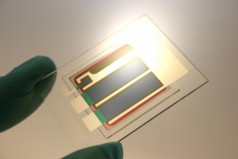 |
| Heliatek world record cells with 12.0% efficiency on an active area of 1.1 cm².
© Heliatek GmbH |
Abstract:
Heliatek GmbH, the leader in organic solar films, today announced a record breaking 12.0% cell efficiency for its organic solar cells. This world record, established in cooperation with the University of Ulm and TU Dresden, was measured by the accredited testing facility SGS. The measurement campaign at SGS also validated the superior low light and high temperature performances of organic photovoltaics (OPV) compared to traditional solar technologies.
Heliatek consolidates its technology leadership by establishing a new world record for organic solar technology with a cell efficiency of 12%
Dresden, Germany | Posted on January 16th, 2013The 12.0% record cell on a standard size of 1.1 cm² combines two patented absorber materials, which convert light of different wavelengths. Using two different absorber materials creates a stronger absorption of photons and improves energetic utilization through a higher photovoltage.Thanks to OPV's unique behavior at high temperatures and low light conditions, this 12% efficiency is comparable to about 14% to 15% efficiency for traditional solar technologies like crystalline silicon and thin film PV. Whereas those technologies significantly lose cell efficiency with rising temperatures and decreasing solar irradiation, organic cells increase their efficiency in these conditions leading to a much higher energy harvesting in real life environments.
"We are pleased to continue to lead the OPV industry with this landmark achievement. Our continuous progress comforts us in our ability to reach 15% efficiency by 2015 and gradually transfer our record efficiencies into Heliatek's roll-to-roll production line. We manufacture solar films and not solar panels. Our customers in the building and construction material industry, in automotive and in light structures, such as shading and street furniture, are integrating these solar films as energy harvesting components to increase the functionality of their products," commented Thibaud Le Séguillon, CEO of Heliatek.
Dr. Martin Pfeiffer, co-founder and CTO of Heliatek, added: "Achieving an unprecedented 12% OPV efficiency is a clear validation of Heliatek's choice not to focus on printed polymers but to go with vacuum deposited oligomers. This technology has been used successfully for OLED displays over the last decade. Vacuum deposition allows for extremely thin yet homogeneous layers down to 5 nm - that is only one ten thousandth of a human hair or twice the size of a strand of a human DNA. With this well-controlled, ultra-thin film process we can deposit a large number of layers on top of each other creating tandem, or even triple junction cells, to absorb a broader spectrum of light."
The new world record efficiency for OPV improves the prior record of 10.7%, which was also set by Heliatek just nine months ago.To achieve this latest leap in cell efficiency, Heliatek capitalized on its in-house R&D know-how and its strong ties to leading universities in the field of OPV. One of the two absorbers was developed and synthesized by Ulm University's Institute of Organic Chemistry II and Advanced Materials, headed by Prof. Peter Bäuerle, co-founder of Heliatek. The cooperation also encompassed Prof. Karl Leo (co-founder of Heliatek) and Dr. Moritz Riede of the 'Institut für Angewandte Photophysik' (IAPP) of 'TU Dresden'. The world record was enabled by significant R&D support from the German Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF-Project LOTsE #03EK3505E), the EU FP7 Program (Project X10D #287818), and the German Research Foundation (DFG Priority Program #1355).
Heliatek's OPV technology based on small molecules (oligomers) is currently being transferred to commercial production. The first production line was launched in spring 2012 and Heliatek Solar Films are already being delivered to industry partners for product development. The commercialization of first partner applications with integrated Heliatek Solar Films as energy harvesting components is expected in late 2013. In parallel, Heliatek has launched a financing round to raise €60 million from current and new investors for a new roll-to-roll volume production line to draw on economies of scale.
####
About Heliatek GmbH
Heliatek was spun-off in 2006 from the Technical University of Dresden and the University of Ulm. The company is the global leader in the development and manufacture of organic solar films based on small molecules. Its business model is to supply custom-designed solar films as energy harvesting components to industries such as building and construction material, automotive, light structure and electronics. Heliatek maintains a total staff of some 63 specialists at its facilities in Dresden and Ulm, Germany. Investors in Heliatek include leading industrial and financial companies such as BASF, Bosch, RWE, Wellington Partners and eCapital. Research and development work, as well as the installation of production technology, has been funded by the Free State of Saxony, the BMBF (Federal Ministry for Education & Research), the BMWi (Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology) and the European Union. Heliatek is currently working on its first roll-to-roll manufacturing line installed in Dresden, Germany, which went into production in the fourth quarter of 2012. It has also kicked off a third financing round to raise €60 million from current and new investors for a new roll-to-roll 75 MWp production line.
About Heliatek's organic solar film technology:
The key to Heliatek's success is the family of small organic molecules - oligomers - developed and synthesized at its own laboratory in Ulm, Germany. Heliatek is the only company in the world that uses the deposition of small organic molecules in a low temperature, roll-to-roll vacuum process. Its organic solar cells are made of nanometers-thin layers of high purity and uniformity. This enables the company to literally engineer the cell architecture to systematically improve efficiency and lifespan. This technology is very similar to the well-established OLED technology (organic LEDs) except that it operates in reverse, taking in light to create electricity. This gives Heliatek access to readily available manufacturing equipment, giving it a fast track to reliable volume production.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Steffanie Rohr
Head of Marketing
Treidlerstraße 3
01139 Dresden, Germany
T (+49-351) 213 034-508
C (+49-173) 359 9693
Copyright © Heliatek GmbH
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








