Home > Press > Graphene membranes may lead to enhanced natural gas production, less CO2 pollution, says CU study
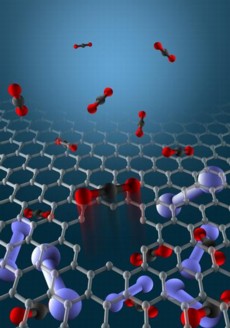 |
| This illustration depicts a single molecular-sized pore in a graphene membrane. The membrane is separating carbon dioxide from nitrogen. A carbon dioxide molecule is passing through the pore while nitrogen molecules are too large to pass through. Illustration by Zhangmin Huang |
Abstract:
Engineering faculty and students at the University of Colorado Boulder have produced the first experimental results showing that atomically thin graphene membranes with tiny pores can effectively and efficiently separate gas molecules through size-selective sieving.
Graphene membranes may lead to enhanced natural gas production, less CO2 pollution, says CU study
Boulder, CO | Posted on October 8th, 2012The findings are a significant step toward the realization of more energy-efficient membranes for natural gas production and for reducing carbon dioxide emissions from power plant exhaust pipes.
Mechanical engineering professors Scott Bunch and John Pellegrino co-authored a paper in Nature Nanotechnology with graduate students Steven Koenig and Luda Wang detailing the experiments. The paper was published Oct. 7 in the journal's online edition.
The research team introduced nanoscale pores into graphene sheets through ultraviolet light-induced oxidative "etching," and then measured the permeability of various gases across the porous graphene membranes. Experiments were done with a range of gases including hydrogen, carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen, methane and sulphur hexaflouride -- which range in size from 0.29 to 0.49 nanometers -- to demonstrate the potential for separation based on molecular size. One nanometer is one billionth of a meter.
"These atomically thin, porous graphene membranes represent a new class of ideal molecular sieves, where gas transport occurs through pores which have a thickness and diameter on the atomic scale," said Bunch.
Graphene, a single layer of graphite, represents the first truly two-dimensional atomic crystal. It consists of a single layer of carbon atoms chemically bonded in a hexagonal "chicken wire" lattice -- a unique atomic structure that gives it remarkable electrical, mechanical and thermal properties.
"The mechanical properties of this wonder material fascinate our group the most," Bunch said. "It is the thinnest and strongest material in the world, as well as being impermeable to all standard gases."
Those characteristics make graphene an ideal material for creating a separation membrane because it is durable and yet doesn't require a lot of energy to push molecules through it, he said.
Other technical challenges will need to be overcome before the technology can be fully realized. For example, creating large enough sheets of graphene to perform separations on an industrial scale, and developing a process for producing precisely defined nanopores of the required sizes are areas that need further development. The CU-Boulder experiments were done on a relatively small scale.
The importance of graphene in the scientific world was illustrated by the 2010 Nobel Prize in physics that honored two scientists at Manchester University in England, Andre K. Geim and Konstantin Novoselov, for producing, isolating, identifying and characterizing graphene. Scientists see a myriad of potential for graphene as research progresses, from making new and better display screens and electric circuits to producing tiny biomedical devices.
The research was sponsored by the National Science Foundation; the Membrane Science, Engineering and Technology Center at CU-Boulder; and the DARPA Center on Nanoscale Science and Technology for Integrated Micro/Nano Electromechanical Transducers at CU-Boulder.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Scott Bunch
303-492-6802
Carol Rowe
303-492-7426
Copyright © University of Colorado at Boulder
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








