Home > Press > The 'living' micro-robot that could detect diseases in humans
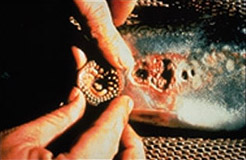 |
| Sea Lamprey1: a Sea Lamprey mouth, close up Copyright 'Great Lakes Fishery Commission' |
Abstract:
A tiny prototype robot that functions like a living creature is being developed which one day could be safely used to pinpoint diseases within the human body.
Called 'Cyberplasm', it will combine advanced microelectronics with latest research in biomimicry (technology inspired by nature). The aim is for Cyberplasm to have an electronic nervous system, 'eye' and 'nose' sensors derived from mammalian cells, as well as artificial muscles that use glucose as an energy source to propel it.
The 'living' micro-robot that could detect diseases in humans
Swindon, UK | Posted on March 29th, 2012The intention is to engineer and integrate robot components that respond to light and chemicals in the same way as biological systems. This is a completely innovative way of pushing robotics forward.
Cyberplasm is being developed over the next few years as part of an international collaboration funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) in the UK and the National Science Foundation (NSF) in the USA. The UK-based work is taking place at Newcastle University. The project originated from a 'sandpit' (idea gathering session) on synthetic biology jointly funded by the two organisations.
Cyberplasm will be designed to mimic key functions of the sea lamprey, a creature found mainly in the Atlantic Ocean. It is believed this approach will enable the micro-robot to be extremely sensitive and responsive to the environment it is put into. Future uses could include the ability to swim unobtrusively through the human body to detect a whole range of diseases.
The sea lamprey has a very primitive nervous system, which is easier to mimic than more sophisticated nervous systems. This, together with the fact that it swims, made the sea lamprey the best candidate for the project team to base Cyberplasm on.
Once it is developed the Cyberplasm prototype will be less than 1cm long. Future versions could potentially be less than 1mm long or even built on a nanoscale.
"Nothing matches a living creature's natural ability to see and smell its environment and therefore to collect data on what's going on around it," says bioengineer Dr Daniel Frankel of Newcastle University, who is leading the UK-based work.
Cyberplasm's sensors are being developed to respond to external stimuli by converting them into electronic impulses that are sent to an electronic 'brain' equipped with sophisticated microchips. This brain will then send electronic messages to artificial muscles telling them how to contract and relax, enabling the robot to navigate its way safely using an undulating motion.
Similarly, data on the chemical make-up of the robot's surroundings can be collected and stored via these systems for later recovery by the robot's operators.
Cyberplasm could also represent the first step on the road to important advances in, for example, advanced prosthetics where living muscle tissue might be engineered to contract and relax in response to stimulation from light waves or electronic signals.
"We're currently developing and testing Cyberplasm's individual components," says Daniel Frankel. "We hope to get to the assembly stage within a couple of years. We believe Cyberplasm could start being used in real-world situations within five years".
The UK element of the Cyberplasm project is a three-year initiative that is receiving EPSRC funding of just over £298,000.
The Cyberplasm team includes:
Professor Joseph Ayers, Northeastern University, USA (animal robots expert)
Professor Vlad Parpura, University of Alabama, USA (neuroscientist)
Professor Chris Voigt, MIT, USA (synthetic biologist)
Dr Daniel Frankel, Newcastle University (bioengineer).
####
About Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
EPSRC is the main UK government agency for funding research and training in engineering and the physical sciences, investing more than £800 million a year in a broad range of subjects – from mathematics to materials science, and from information technology to structural engineering. www.epsrc.ac.uk
About NSF
NSF is an independent federal agency created by the US Congress in 1950. With an annual budget of about $6.9 billion (FY 2010), it is the funding source for approximately 20 per cent of all federally-supported basic research conducted by America's colleges and universities. In many fields, such as mathematics, computer science and the social sciences, NSF is the major source of federal backing. www.nsf.gov
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
EPSRC Press Office
44 01-793-444-404
Dr Daniel Frankel
School of Chemical Engineering and Advanced Materials
Newcastle University
Tel:44 0191-222-6782
Copyright © Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Synthetic Biology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








