Home > Press > A simple slice of energy storage: Rice University lab uses lasers to write supercapacitors on sheets of graphite oxide
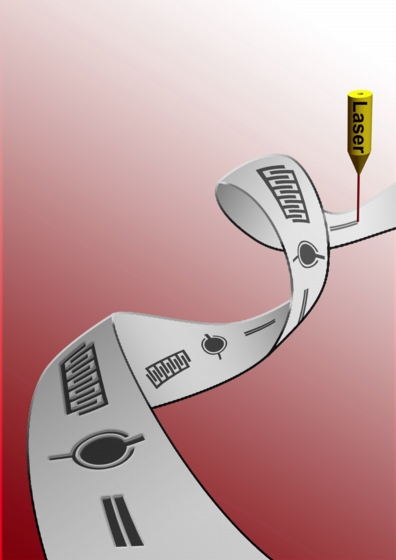 |
| Burning patterns into graphite oxide with a laser turns the thin sheets into fully functional supercapacitors, according to a new paper by Rice University scientists in Nature Nanotechnology. (Credit: Ajayan Lab/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Turning graphite oxide (GO) into full-fledged supercapacitors turns out to be simple. But until a laboratory at Rice University figured out how, it was anything but obvious.
A simple slice of energy storage: Rice University lab uses lasers to write supercapacitors on sheets of graphite oxide
Houston, TX | Posted on August 1st, 2011Rice Professor Pulickel Ajayan and his team discovered they could transform a sheet of GO into a functional supercapacitor by writing patterns into it with a laser. Scientists already knew that the heat of a laser could convert GO -- the oxidized form of graphite, or carbon-based pencil lead -- into electrically conducting reduced graphite oxide (RGO). By writing patterns of RGO into thin sheets of GO, the Rice researchers effectively turned them into free-standing supercapacitors with the ability to store and release energy over thousands of cycles.
The discovery was reported this week in the online edition of Nature Nanotechnology.
The surprising find was that GO, when hydrated, can hold ions and serve as a solid electrolyte and an electrically insulating separator. "This is quite easy, as GO soaks up water like a sponge and can hold up to 16 percent of its weight," said Wei Gao, lead author of the paper and a graduate student in the Ajayan Lab.
"The fundamental breakthrough here is that GO, when it contains water, acts as an ionic conductor," said Ajayan, Rice's Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science and of chemistry. "So we're able to convert a sheet of GO into a supercapacitor without adding anything. All you need are a pattern and the electrodes, and you have a device. Of course the devices also perform in the presence of external electrolytes, which is even better.
"I think you're going to see a lot of tiny devices that need smaller power sources. Intermediate-sized devices might also be powered by this material; it's very scalable."
As a control experiment, the team sucked all the water out of an RGO-GO-RGO device in a vacuum to kill its ionic conductivity. Exposing it to air for three hours completely restored its supercapacitor function, another potentially handy characteristic.
To build a fully functional supercapacitor, conducting electrode materials need to be separated by an insulator that contains the electrolyte. When laser-written patterns of conducting RGO are separated by GO, the material becomes an energy storage device, Gao said. The patterns can be layered top and bottom or on the same plane.
In their experiments, heat from a laser at Rice's Oshman Engineering Design Kitchen sucked oxygen out of the surface to create the dark, porous RGO, which provided a level of resistance and restrained the GO-contained ions until their controlled release. Patterns were written in the GO with nearly one-micron accuracy.
Essentially, the devices exhibited good electrochemical performance -- without the chemicals.
Testing of the devices at Rice and by colleagues at the University of Delaware showed their performance compares favorably with existing thin-film micro-supercapacitors. They exhibit proton transport characteristics similar to that of Nafion, a commercial electrolyte membrane discovered in the 1960s, Ajayan said.
While the lab won't make flat supercapacitors in bulk anytime soon, Ajayan said the research opens the way to interesting possibilities, including devices for use in fuel cells and lithium batteries.
He said the discovery is surprising "because a lot of people have been looking at graphite oxide for five or 10 years now, and nobody has seen what we see here. We've discovered a fundamental mechanism of graphite oxide -- an ionic conducting membrane -- that is useful for applications."
Co-authors of the paper are graduate student Neelam Singh, former postdoctoral researcher Li Song and Lijie Ci, postdoctoral researcher Zheng Liu, research scientist Arava Leela Mohana Reddy and Robert Vajtai, a faculty fellow in mechanical engineering and materials science, all of Rice; and graduate student Qing Zhang and Binngqing Wei, an associate professor of mechanical engineering, both at the University of Delaware.
Nanoholdings LLC funded the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 285-acre forested campus in Houston, Texas, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is known for its "unconventional wisdom." With 3,485 undergraduates and 2,275 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is less than 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 4 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to futureowls.rice.edu/images/futureowls/Rice_Brag_Sheet.pdf .
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








