Home > Press > NIST 'Nanowire' Measurements Could Improve Computer Memory
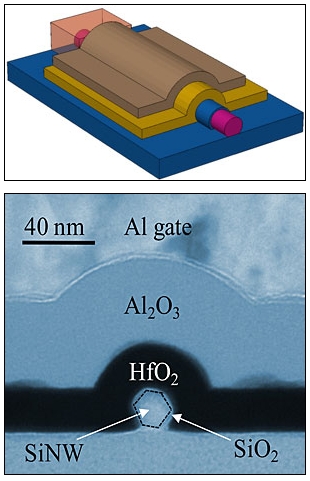 |
| In this schematic image (top) and transmission electron micrograph, a silicon nanowire is shown surrounded by a stack of thin layers of material called dielectrics, which store electrical charge. NIST scientists determined the best arrangement for this dielectric stack for the optimal construction of silicon nanowire-based memory devices. Credit: Schematic Zhu, GMU. TEM Bonevich, NIST. |
Abstract:
A recent study* at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) may have revealed the optimal characteristics for a new type of computer memory now under development. The work, performed in collaboration with researchers from George Mason University (GMU), aims to optimize nanowire-based charge-trapping memory devices, potentially illuminating the path to creating portable computers and cell phones that can operate for days between charging sessions.
NIST 'Nanowire' Measurements Could Improve Computer Memory
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on May 20th, 2011The nascent technology is based on silicon formed into tiny wires, approximately 20 nanometers in diameter. These "nanowires" form the basis of memory that is non-volatile, holding its contents even while the power is off—just like the flash memory in USB thumb drives and many mp3 players. Such nanowire devices are being studied extensively as the possible basis for next-generation computer memory because they hold the promise to store information faster and at lower voltage.
Nanowire memory devices also hold an additional advantage over flash memory, which despite its uses is unsuitable for one of the most crucial memory banks in a computer: the local cache memory in the central processor.
"Cache memory stores the information a microprocessor is using for the task immediately at hand," says NIST physicist Curt Richter. "It has to operate very quickly, and flash memory just isn't fast enough. If we can find a fast, non-volatile form of memory to replace what chips currently use as cache memory, computing devices could gain even more freedom from power outlets—and we think we've found the best way to help silicon nanowires do the job."
While the research team is by no means the only lab group in the world working on nanowires, they took advantage of NIST's talents at measurement to determine the best way to design charge-trapping memory devices based on nanowires, which must be surrounded by thin layers of material called dielectrics that store electrical charge. By using a combination of software modeling and electrical device characterization, the NIST and GMU team explored a wide range of structures for the dielectrics. Based on the understanding they gained, Richter says, an optimal device can be designed.
"These findings create a platform for experimenters around the world to further investigate the nanowire-based approach to high-performance non-volatile memory," says Qiliang Li, assistant professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at GMU. "We are optimistic that nanowire-based memory is now closer to real application."
* X. Zhu, Q. Li, D. Ioannou, D. Gu, J.E. Bonevich, H. Baumgart, J. Suehle and C.A. Richter. Fabrication, characterization and simulation of high performance Si nanowire-based non-volatile memory cells. Nanotechnology, May 16, 2011, 22 254020 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/25/254020.
####
About NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chad Boutin
301-975-4261
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








