Home > Press > Purdue, NIST working on breathalyzers for medical diagnostics
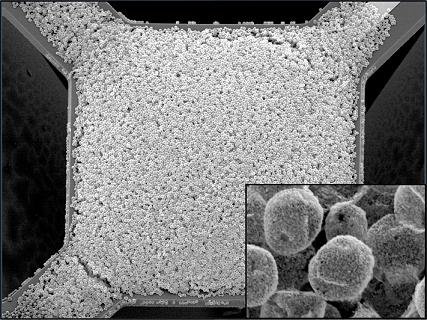 |
| This image shows a new type of sensor for an advanced breath-analysis technology that rapidly diagnoses patients by detecting "biomarkers" in a person's respiration in real time. Researchers used a template made of micron-size polymer particles and coated them with much smaller metal oxide nanoparticles. Using nanoparticle-coated microparticles instead of a flat surface allows researchers to increase the porosity of the sensor films, increasing the "active sensing surface area" to improve sensitivity. (Purdue University and NIST) |
Abstract:
Researchers have overcome a fundamental obstacle in developing breath-analysis technology to rapidly diagnose patients by detecting chemical compounds called "biomarkers" in a person's respiration in real time.
Purdue, NIST working on breathalyzers for medical diagnostics
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on January 3rd, 2011The researchers demonstrated their approach is capable of rapidly detecting biomarkers in the parts per billion to parts per million range, at least 100 times better than previous breath-analysis technologies, said Carlos Martinez, an assistant professor of materials engineering at Purdue who is working with researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
"People have been working in this area for about 30 years but have not been able to detect low enough concentrations in real time," he said. "We solved that problem with the materials we developed, and we are now focusing on how to be very specific, how to distinguish particular biomarkers."
The technology works by detecting changes in electrical resistance or conductance as gases pass over sensors built on top of "microhotplates," tiny heating devices on electronic chips. Detecting biomarkers provides a record of a patient's health profile, indicating the possible presence of cancer and other diseases.
"We are talking about creating an inexpensive, rapid way of collecting diagnostic information about a patient," Martinez said. "It might say, 'there is a certain percentage that you are metabolizing a specific compound indicative of this type of cancer,' and then additional, more complex tests could be conducted to confirm the diagnosis."
The researchers used the technology to detect acetone, a biomarker for diabetes, with a sensitivity in the parts per billion range in a gas mimicking a person's breath.
Findings were detailed in a research paper that appeared earlier this year in the IEEE Sensors Journal, published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers' IEEE Sensors Council. The paper was co-authored by Martinez and NIST researchers Steve Semancik, lead author Kurt D. Benkstein, Baranidharan Raman and Christopher B. Montgomery.
The researchers used a template made of micron-size polymer particles and coated them with far smaller metal oxide nanoparticles. Using nanoparticle-coated microparticles instead of a flat surface allows researchers to increase the porosity of the sensor films, increasing the "active sensing surface area" to improve sensitivity.
A droplet of the nanoparticle-coated polymer microparticles was deposited on each microhotplate, which are about 100 microns square and contain electrodes shaped like meshing fingers. The droplet dries and then the electrodes are heated up, burning off the polymer and leaving a porous metal-oxide film, creating a sensor.
"It's very porous and very sensitive," Martinez said. "We showed that this can work in real time, using a simulated breath into the device."
Gases passing over the device permeate the film and change its electrical properties depending on the particular biomarkers contained in the gas.
Such breathalyzers are likely a decade or longer away from being realized, in part because precise standards have not yet been developed to manufacture devices based on the approach, Martinez said.
"However, the fact that we were able to do this in real time is a big step in the right direction," he said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Source:
Carlos Martinez
765-494-3271
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchersí approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchersí approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








