Home > Press > Molecule-sized bait used by UCLA research team to fish for new drug targets
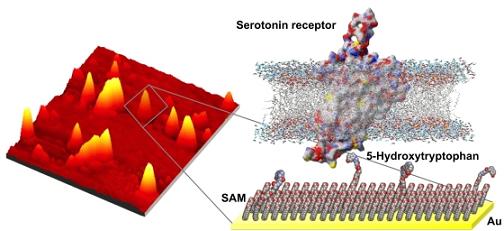 |
| Fishing for molecules (Left) Atomic force microscopy image of serotonin precursor-modified surface with captured serotonin receptor-containing nanovesicles. (Right) Illustration of the molecular structures of the surface chemistry and the relative size differences between the "bait" (5-hydroxytryptophan) and the membrane-associated serotonin receptors selectively captured by these surfaces. |
Abstract:
The technique could lead to a new generation of psychiatric medications
By Mike Rodewald
Molecule-sized bait used by UCLA research team to fish for new drug targets
Los Angeles, CA | Posted on May 15th, 2010UCLA researchers and their collaborators have developed a method that could open the door for investigations into the function of half of all proteins in the human body.
The research team has demonstrated nanoscale control over molecules, allowing for the precise study of interactions between proteins and small molecules. Their new technique, in which molecules are used as bait to capture and study large biomolecules, could lead to a new generation of psychiatric medications.
In a paper published last month in the journal ACS Chemical Neuroscience, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from UCLA and the Pennsylvania State University (PSU) report on their investigation of the interactions between large biomolecules, which include DNA and proteins, and small molecules, which include hormones and neurotransmitters such as serotonin.
The research team, led by Anne Andrews, professor of psychiatry and a researcher at both the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior at UCLA and UCLA's California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI), is studying these interactions to identify a new generation of targets, or key molecules that correspond to specific diseases or conditions.
Interactions between large biomolecules and small molecules are ubiquitous in nature; they are the method for communication within and between cells. But these interactions have proven difficult to isolate in a laboratory setting. Increased understanding of these interactions is vital for the development of new medications for psychiatric disorders, the researchers say.
"Currently, little is known about which targets apply to specific diseases," Andrews said. "Pharmaceutical companies are very good at designing medications once they have a target to go after; my group is working on providing them with targets."
Up to this point, drug development for psychiatric disorders such as depression has been a trial-and-error process in which pharmaceutical companies refine new drugs based on a few existing drugs that were discovered accidentally. Andrews said she hopes that her team's research will lead to more effective treatments, because current depression medications only work for 30 to 50 percent of the population.
Nanoscale control is the key to the UCLA-Penn State team's findings. Their breakthrough capitalizes on work by the research group of co-author Paul Weiss on patterning self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), single layers of molecules that orient themselves on flat surfaces. Weiss, a distinguished professor of chemistry and biochemistry who holds UCLA's Fred Kavli Chair in Nanosystems Sciences, and others discovered that SAMs don't actually form perfect surfaces. They contain defects, which can in turn be used to isolate single molecules.
"Currently we are able to space defects out over a surface. We then use these defects to control the placement and environment of the individual functional molecules," said Weiss, who is also director of the CNSI.
Even spacing is important because the UCLA-Penn State team placed serotonin, a small molecule, in defects to act as bait to capture and study large molecules. If the defects are not widely spaced, there is not enough space between serotonin molecules for each to capture a large molecule.
Large biomolecule and small molecule interactions have proved notoriously difficult to study using previous methods. When the SAM fishing pole baited with serotonin captures a large molecule, the research team is able to study the interactions in a way that replicates the molecules' natural interactions.
####
About California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA
The California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA is an integrated research center operating jointly at UCLA and UC Santa Barbara whose mission is to foster interdisciplinary collaborations for discoveries in nanosystems and nanotechnology; train the next generation of scientists, educators and technology leaders; and facilitate partnerships with industry, fueling economic development and the social well-being of California, the United States and the world. The CNSI was established in 2000 with $100 million from the state of California and an additional $250 million in federal research grants and industry funding. At the institute, scientists in the areas of biology, chemistry, biochemistry, physics, mathematics, computational science and engineering are measuring, modifying and manipulating the building blocks of our world — atoms and molecules. These scientists benefit from an integrated laboratory culture enabling them to conduct dynamic research at the nanoscale, leading to significant breakthroughs in the areas of health, energy, the environment and information technology.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts
Jennifer Marcus
310-267-4839
Mike Rodewald
310-267-5883
Copyright © California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








