Home > Press > Arsenic and Gold Clusters
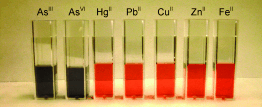 |
| Low level: The amount of arsenic in Bangladeshi well water and in bottled drinking water and Mississippi tap water are indicated by a dynamic light scattering (DLS) assay. Label-free gold nanoparticles are used in a selective colorimetric assay (see picture) and in a highly sensitive DLS assay for the recognition of arsenic in concentrations as low as 3 ppt. |
Abstract:
Fast, easy, and highly sensitive arsenic detection with gold nanoparticles
Arsenic and Gold Clusters
Jackson, MI | Posted on November 25th, 2009Mention of arsenic poisoning usually brings to mind underhanded murder. However, the danger of arsenic poisoning from contaminated drinking water is far greater. Low concentrations of arsenic are found in nearly all soils and thus also in ground water. About 140 million people worldwide possibly drink water that contains arsenic concentrations above the WHO-recommended limit of 10 ppb (parts per billion). Researchers at Jackson State University (MS, USA) have now developed a new approach for a rapid, easy, and highly sensitive arsenic test. As Paresh Chandra Ray's team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie, their method is based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles, and it selectively detects arsenic in drinking water down to concentrations of 3 ppt (parts per trillion).
Countries like India, Bangladesh, and Thailand are primarily affected by ground water with high arsenic concentrations. However, high concentrations of arsenic have also been found in some areas of North and South America. Once detected, the problem can fairly easily be addressed. Current analytical techniques are time-consuming and require a series of enrichment steps.
The new process could now speed up and simplify arsenic analysis. The scientists working with Ray have attached special organic molecules to the surfaces of gold nanoparticles. These molecules act as "ligands" for arsenic, meaning that they form a complex with it. Each arsenic ion can bind to three ligands, which allows it to link together up to three gold particles. The higher the arsenic concentration in the sample, the more strongly the gold particles clump together and the number of bigger aggregates increases. The color of gold nanoparticles in a liquid depends on their size. Whereas the arsenic-free gold nanoparticles appear red, arsenic-induced aggregation causes the color to change to blue. Concentrations down to 1 ppb can be detected with the naked eye by means of the color change. Arsenic binds to the ligands much more strongly than other metals; the researchers were able to increase this selectivity by attaching three different ligands to the gold.
One very precise method for detecting minimal changes in particle size is dynamic light scattering (DLS), in which laser light scattered by the particles is analyzed. By using DLS, Ray and his co-workers were able to detect and quantify arsenic concentrations as low as 3 ppt. In samples of well water from Bangladesh, the team found 28 ppb arsenic; in water from taps in Jackson (Mississippi, USA) they found 380 ppt.
Author: Paresh Chandra Ray, Jackson State University (USA), chem.jsums.edu/ray/
Title: Use of Gold Nanoparticles in a Simple Colorimetric and Ultrasensitive Dynamic Light Scattering Assay: Selective Detection of Arsenic in Groundwater
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2009, 48, No. 51, 9668-9671, doi: 10.1002/anie.200903958
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Angewandte Chemie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Sensors
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








