Home > Press > The guiding of light: A new metamaterial device steers beams along complex pathways: Boston College discovery bends light around corners, along Eastern seaboard
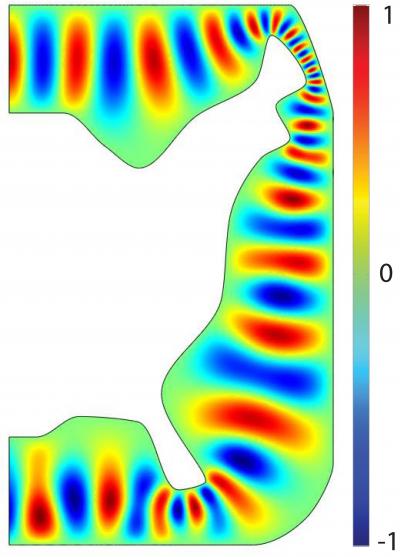 |
| Boston College researchers report developing a device that can bend light along complex pathways. An illustration shows a simulated electromagnetic wave propagation. Guided by a set of instructions delivered by the device, the wave curves around the profile of the eastern US while behaving as if traveling in a straight line.
Credit: Optics Express |
Abstract:
Using a composite metamaterial to deliver a complex set of instructions to a beam of light, Boston College physicists have created a device to guide electromagnetic waves around objects such as the corner of a building or the profile of the eastern seaboard.
The guiding of light: A new metamaterial device steers beams along complex pathways: Boston College discovery bends light around corners, along Eastern seaboard
Boston, MA | Posted on August 1st, 2009As directed by the researchers' novel device, these beams continue to behave as if traveling in a straight line. In one computer simulation, Assistant Professor of Physics Willie J. Padilla and researcher Nathan Landy revealed the device could steer a beam of light along the boundary of the US, stretching from Michigan to Maine, down the seaboard, around Florida and into the Louisiana bayou, the researchers report in the upcoming edition of the journal Optics Express.
The researchers accomplished their feat by developing a much more precise set of instructions, which create a grid-like roadmap capable of twisting and turning a beam of light around objects or space. Their discovery is an extension of earlier metamaterial "cloaking" techniques, which have conjured up images of the Harry Potter character disappearing beneath his invisibility cloak.
Padilla and Landy report developing a space-mapping technique that delivers greater precision and efficiency guiding light along pathways that previously were too complex to sustain - from 90-degree angles to the rugged coastal profile of Maine. Furthermore, they've built this new device using relatively common dielectric materials, such as silicon.
"Our method combines the novel effects of transformational optics with the practicality of dielectric construction," Padilla and Landy report. "We show that our structures are capable of guiding light in an almost arbitrary fashion over an unprecedented range of frequencies."
The discovery builds upon a decade-long revolution in electromagnetics brought about by the emergence of metamaterials. Constructed from artificial composites, metamaterials have exhibited effects such as directing light at a negative index of refraction.
Researchers have combined metamaterials with artificial optical devices - also known as transformational optics - to demonstrate the "invisibility cloak" effect, essentially directing light around a space and effectively masking its existence. In addition, other researchers have used a method known as quasi-conformal mapping and very complex metamaterials to issue a somewhat imprecise set of instructions that create another space-cloaking effect.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ed Hayward
617-552-4826
Copyright © Boston College
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








