Home > Press > Connecting materials science with biology, K-State engineers create DNA sensors that could identify cancer using material only one atom thick
 |
Abstract:
Kansas State University engineers think the possibilities are deep for a very thin material.
Vikas Berry, assistant professor of chemical engineering, is leading research combining biological materials with graphene, a recently developed carbon material that is only a single atom thick.
Connecting materials science with biology, K-State engineers create DNA sensors that could identify cancer using material only one atom thick
MANHATTAN, KS | Posted on April 13th, 2009"The biological interfacing of graphene is taking this material to the next level," Berry said. "Discovered only four years ago, this material has already shown a large number of capabilities. K-Staters are the first to do bio-integrated research with graphene."
To study graphene, researchers rely on an atomic force microscope to help them observe and manipulate these single atom thick carbon sheets.
"It's a fascinating material to work with," Berry said. "The most significant feature of graphene is that the electrons can travel without interruptions at speeds close to that of light at room temperature. Usually you have to go near zero Kelvin -- that's about 450 degrees below zero Fahrenheit -- to get electrons to move at ultra high speeds."
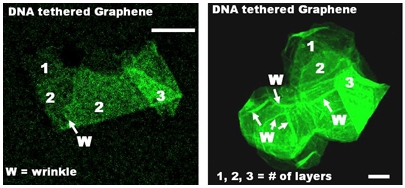
One of Berry's developments is a graphene-based DNA sensor. When electrons flow on the graphene, they change speed if they encounter DNA. The researchers notice this change by measuring the electrical conductivity. The work was published in Nano-Letters.
"Most DNA sensors are optical, but this one is electrical," Berry said. "We are currently collaborating with researchers from Harvard Medical School to sense cancer cells in blood."
Another area he is exploring is loading graphene with antibodies and flowing bacteria across the surface.
"Most researchers focus on pristine graphene, but we're making it dirty," he said.
Berry and Nihar Mohanty, a graduate student in chemical engineering, used a type of bacteria commonly found in rice and interfaced it with graphene. They found that the graphene with tethered antibodies will wrap itself around an individual bacterium, which remains alive for 12 hours.
Berry said that possible applications include a high-efficiency bacteria-operated battery, where by using geobater, a type of bacteria known to produce electrons, can be wrapped with graphene to produce electricity. The research was presented at the annual American Physical Society conference in Pittsburgh and the American Institute for Chemical Engineers conference in Philadelphia.
"Materials science is an incredible field with several exploitable quantum effects occurring at molecular scale, and biology is a remarkable field with a variety of specific biochemical mechanisms," Berry said. "But for the most part the two fields are isolated. If you join these two fields, the possibilities are going to be immense. For example, one can think of a bacterium as a machine with molecular scale components and one can exploit the functioning of those components in a material device."
For his doctoral research, Berry used bacteria to make a humidity sensor.
"That was only possible through combining materials science with biological science," he said.
Another area of his current research is compressing and stretching molecular-junctions between nanoparticles. Berry said that his group has developed a molecular-spring device where they can compress and stretch molecules, which then act like springs, allowing researchers to study how they relax back. He said that this technology could be used to create molecular-timers in which the spring action from a decompressed molecule on a chip could trigger a circuit, for instance.
Berry said for stretching the molecules, Kabeer Jasuja, a doctoral student in chemical engineering, came up with the idea to place the device on a centrifuge to stretch the molecules with centrifugal force.
The work was published in the journal Small.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Source:
Vikas Berry
785-532-5519
News release prepared by:
Erinn Barcomb-Peterson
785-532-6415
Copyright © Kansas State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








