Home > Press > Surprise shift: A first-of-a-kind switch in chemical bonding by a zirconium atom spotted by scientists
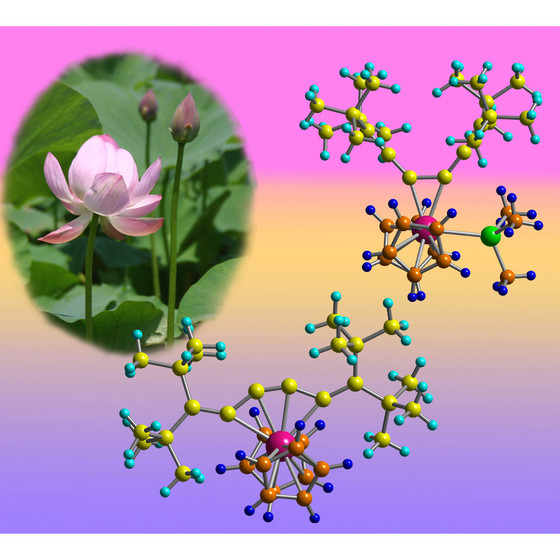 |
| Figure 1: Schematic showing that adding or removing an extra chemical group (green) to the zirconium atom (pink) can open and close the structure of the molecule like the petals of a lotus flower. |
Abstract:
A zirconium atom can switch easily between two different bonding patterns in an unusual molecule created by Japanese scientists.
Surprise shift: A first-of-a-kind switch in chemical bonding by a zirconium atom spotted by scientists
Japan | Posted on April 12th, 2009The molecule's odd behavior is the first example of this particular type of chemical bonding shift, according to Noriyuki Suzuki of RIKEN's Advanced Science Institute in Wako, and his colleagues at Saitama University and Saitama Institute of Technology. "These complexes have very unique structures and show interesting movement," says Suzuki. An example is shown in Figure 1.
The team discovered the phenomenon when they were experimenting with a molecule (hexapentaene) made from a chain of six carbon atoms, all doubly bonded to each other. The chain is surrounded by a long cloud of delocalized electrons, which can bond with a zirconium-based compound to create a new complex.
Once the new complex has formed, the zirconium atom normally tends to bridge between carbon atoms in different parts of the chain, creating a five-membered ring. But when very bulky groups were added to each end of the chain, the zirconium switches its allegiance so that it sticks to just the central carbon-carbon double bond.
The complex could be toggled between its two bonding modes by adding or removing other chemical groups such as phosphines around the zirconium atom. Further experiments showed that this sort of shift was the first step in a reaction the scientists had previously studied, where adding an isocyanide chemical to the zirconium complex created a compound with a small ring of four carbon atoms at its heart.
This switching behavior is well known in certain ring-shaped organic molecules, but is much rarer in these molecular chains, and is unprecedented with this particular compound. "It suggests the possibility of a molecular motion like scissors or tongs," says Suzuki. The research is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society1.
Suzuki's team has spent several years investigating a range of such zirconium complexes, which were long assumed to be too unstable to isolate2,3.
Although there are no immediate applications for this family of complexes, Suzuki suggests that it may be possible to use the scissoring action identified in their latest research to capture another molecule or ion. "We might be able to achieve a molecular machine that catches a certain target," says Suzuki.
Reference
1. Suzuki, N., Hashizume, D., Yoshida, H., Tezuka, M., Ida, K., Nagashima, S. & Chihara, T. Reversible haptotropic shift in zirconocene-hexapentaene complexes. Journal of the American Chemical Society 131, 2050-2051(2009) .
2. Suzuki, N., Nishiura, M. & Wakatsuki, Y. Isolation and structural characterization of 1-zirconacyclopent-3-yne, five-membered cyclic alkynes. Science 295, 660-663 (2002).
3. Suzuki, N., Hashizume, D., Koshino, H. & Chihara, T. Transformation of a 1-zirconacyclopent-3-yne, a five-membered cycloalkyne, into a 1-zirconacyclopent-3-ene and formal "1-zirconacyclopenta-2,3-dienes". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 47, 5198-5202 (2008).
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the RIKEN Chemical Analysis Team
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Riken
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








