Home > Press > Argonne scientists pinpoint mechanism to increase magnetic response of ferromagnetic semiconductor under high pressure
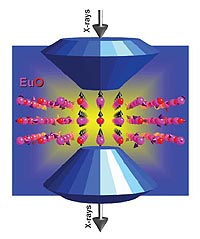 |
| A ferromagnetic-semiconductor europium oxide sample is subjected to high pressures in a diamond anvil cell. The electronic structure is simultaneously probed with circularly polarized X-rays at the Advanced Photon Source, revealing the mechanism responsible for the strengthening of magnetic interactions under pressure. |
Abstract:
Europium oxide may help usher in next generation of microelectronics
Argonne scientists pinpoint mechanism to increase magnetic response of ferromagnetic semiconductor under high pressure
ARGONNE, IL | Posted on March 2nd, 2009When squeezed, electrons increase their ability to move around. In compounds such as semiconductors and electrical insulators, such squeezing can dramatically change the electrical and magnetic properties.
Under ambient pressure, europium oxide (EuO) becomes ferromagnetic only below 69 Kelvin, limiting its applications. However, its magnetic ordering temperature is known to increase with pressure, reaching 200 Kelvin when squeezed by 150,000 atmospheres. The relevant changes in electronic structure responsible for such dramatic changes, however, remained elusive until recently.
Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory have manipulated electron mobility and pinpointed the mechanism controlling the strength of magnetic interactions and, hence, the material's magnetic ordering temperature.
"EuO is a ferromagnetic semiconductor and is a material that can carry spin polarized currents, which is an integral element of future devices aimed at manipulating both the spin and the charge of electrons in new generation microelectronics," said Argonne postdoctoral researcher Narcizo Souza-Neto.
Using powerful X-rays from the Advanced Photon Source to probe the material's electronic structure under pressure, Souza-Neto and Argonne physicist Daniel Haskel reported in the February 6 issue of Physical Review Letters that localized, 100 percent polarized Eu 4f electrons become mobile under pressure by hybridizing with neighboring, extended electronic states. The increased mobility enhances the indirect magnetic coupling between Eu spins resulting in a three-fold increase in the ordering temperature. The paper, "Pressure-induced electronic mixing and enhancement of ferromagnetic ordering in EuX (X=O,S,Se,Te) magnetic semiconductors," is available online.
While the need for large applied pressures may seem a burden for applications, large compressive strains can be generated at interfacial regions in EuO films by varying the mismatch in lattice parameter with selected substrates. By pinpointing the mechanism the research provides a road map for manipulating the ordering temperatures in this and related materials, e.g., through strain or chemical substitutions with the ultimate goal of reaching 300 Kelvin (room temperature).
"Manipulation of strain," Haskel said, "adds a new dimension to the design of novel devices based on injection, transport and detection of high spin-polarized currents in magnetic/semiconductor hybrid structures."
Other authors in the paper are graduate student Yuan-Chieh Tseng (Northwestern University) and Gerard Lapertot (CEA-Grenoble).
Funding for this research was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science, the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States.
####
About Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America 's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
Follow Argonne on Twitter at twitter.com/argonne.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brock Cooper
630/252-5565
Copyright © Argonne National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








