Home > Press > Water: More Than Just a Drink
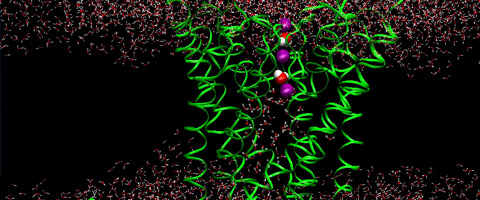 |
| To understand electrical activity of nerve cells, the Asthagiri Lab develops simulations that show selectivity of channel proteins (in green) for potassium ions (in purple). Credit: Asthagiri Group / JHU |
Abstract:
In his book "Life's Matrix: A biography of water," author and Nature consulting editor Philip Ball declares that water is the "weirdest liquid." Dilip Asthagiri, assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, would agree. "There are very many puzzling features in all of aqueous chemistry and biology," says Asthagiri, an affiliated faculty member of the Institute for NanoBioTechnology. With a sub nanoscale diameter of about 3 Angstroms (0.3 nanometer), Asthagiri says, the water molecule is "more ‘nano' than nano" and an understanding of water is integral to this emerging science.
Water: More Than Just a Drink
Baltimore, MD | Posted on June 10th, 2008Despite the fact that scientists have been studying water and its properties for about two centuries, Asthagiri says, it has only been in the last 15 years or so that a framework of knowledge has begun to emerge, one that attempts to connect the chemical nature of interactions in water with the physics of the aqueous solution. His particular field of research—hydration and how it affects the interaction between water and the substances dissolved in it (solutes)—is just a piece of this puzzle.
"We are trying to understand water, why solutes behave the way they do in water, and how hydration affects proteins," he says. And although he and his students study water, his labs are far from wet. The students use complex mathematical modeling to investigate why solutes behave the way they do.
Take for example, the Hofmeister effect, named for the scientist who in 1888 observed that some salts will cause a protein to fall out of solution, while others will increase protein solubility. The reasons for this behavior are not well understood.
"Protein solubility, which is an important matter for pharmaceutical companies, will be different in sodium chloride than it will be in potassium chloride, even if you adjust the concentrations of the salt to be the same." Asthagiri explains. "So there is something in the way the sodium ion interacts with water and the way the potassium ion interacts with water that is causing the difference. There is currently no compelling theory to explain this phenomenon."
Studying these properties may not seem very "sexy," Asthagiri says, but chemistry and biology are full of such conundrums. "If I want to make any progress, I will have to address them."
Before coming to Johns Hopkins, Asthagiri worked at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, where he was first a postdoctoral researcher and then a staff scientist. He says his move to Hopkins has allowed him the opportunity to interact with students as a mentor and teacher. Currently, Asthagiri has three graduate students and says he is happiest when heavily involved in the development of his students' projects.
For more information on the Asthagiri lab, visit: http://shiva.che.jhu.edu/index.html
Lamia Wahba, pre-doctoral student in biology and a member of the Institute for NanoBioTechnology's IGERT program, contributed to this article, which was written as part of the Intersession 2008 course requirements of Science Writing for Scientists and Engineers. IGERT stands for Integrative Graduate Education and Research Traineeship.
####
About Institute for NanoBioTechnology
The Institute for NanoBioTechnology at Johns Hopkins University is revolutionizing health care by bringing together internationally renowned expertise in medicine, engineering, the sciences, and public health to create new knowledge and groundbreaking technologies.
INBT programs in research, education, outreach, and technology transfer are designed to foster the next wave of nanobiotechnology innovation.
Approximately 155 faculty are affiliated with INBT and are also members of the following Johns Hopkins institutions: Krieger School of Arts and Sciences, Whiting School of Engineering, School of Medicine, Bloomberg School of Public Health, and Applied Physics Laboratory.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
* Institute for NanoBioTechnology
214 Maryland Hall
3400 North Charles Street
Baltimore, MD 21218
* Email:
* Phone: (410) 516-3423
* Fax: (410) 516-2355
Copyright © Institute for NanoBioTechnology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








