Home > Press > Symposium to Explore Role Nanoparticles May Play in Disease
 |
| John Lieske, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine |
Abstract:
Two Mayo Clinic researchers who study the role nanoparticles may play in hardening of the arteries and in the formation of kidney stones, will lead a symposium on how these super-small particles may affect the body's physiology. The symposium will take place April 8 at the Experimental Biology conference in San Diego.
Symposium to Explore Role Nanoparticles May Play in Disease
Bethesda, MD | Posted on April 3rd, 2008Nanoparticles are a thousand times smaller than the bacteria, E. coli, but recent advances in microscopy have allowed researchers to watch them interact with cells in the body, said Virginia M. Miller and John C. Lieske of the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine. They will lead the symposium, "Using nanotechnology to answer physiological questions."
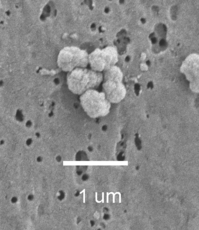
One of the questions physiologists want to explore is whether nanoparticles can cause diseases such as atherosclerosis, kidney stones, gall stones and periodontal disease. Dr. Lieske is investigating how nano-sized crystals in the kidney can lead to the development of kidney stones. Dr. Miller has been studying the link between atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and nanoparticles which calcify within the arteries.
A fuller audio interview with the researchers is available at http://www.lifelines.tv. (Episode 7)
New technology: promise and peril?
Nanotechnology presents intriguing possibilities and some troubling unknowns. The technology is already applied in commercial products as disparate as flame resistant materials and cosmetics. In addition, the technology holds promise in the development of medications that can target precise areas of the body, such as a tumor.
Because of their size, nanoparticles may more easily gain entry to the body, where the longterm effects are unknown. Dr. Miller has found that some nanoparticles cause inflammation when injected into the blood vessels of animals, an early step in the development of atherosclerosis.
Using the latest in microscopy, Dr. Miller has begun to observe nanoparticles from atherosclerotic tissue. She hopes to determine how these particles gain access to cells and whether the interaction eventually leads to cell activation or death leading to calcification.
Kidneys stones start as tiny calcifications which later become larger and eventually develop into kidney stones. Dr. Lieske hypothesizes that the nanoparticle causes the initial calcification. Once that happens, other processes can take place that results in a kidney stone.
It is not yet known where nanoparticles that are implicated in kidney stones and atherosclerosis originate - whether our bodies contain them naturally or we obtain them from the environment.
Miller said research should proceed to determine if nanoparticles are safe over the long term. "We may not know some of the consequences until further down the road" she said.
Dr. Miller and Dr. Lieske will moderate a program on nanotechnology at Experimental Biology. The speakers are Vitaly Vodyanoy of the University of Auburn; Robert Lee of The Ohio State University; Kevin D. Gillis of the University of Missouri-Columbia and Farooq Shiekh of the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine will present at the symposium.
Editor's Notes: To arrange an interview with Dr. Lieske or Dr. Miller, please contact Christine Guilfoy at or (301) 634-7253. A portion of the interview with these researchers can be found on Life Lines, the podcast of The American Physiological Society. You can find it at www.lifelines.tv.
Physiology is the study of how molecules, cells, tissues and organs function to create health or disease. The American Physiological Society (www.the-aps.org) has been an integral part of this scientific discovery process since it was established in 1887.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Christine Guilfoy
(301) 634-7253
Copyright © Newswise
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Events/Classes
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








