Home > Press > The Library of Congress in Your Wrist Watch?
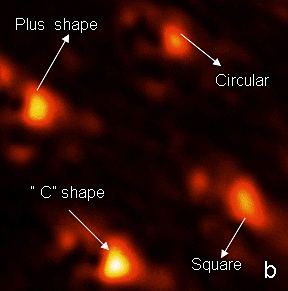 |
| Photo Caption: Researchers focused laser light on 30-nanometer spots using various apertures. The c-shaped aperture produced the most powerful result as seen in this scanning near-field optical microscope image by researcher Rabee Ikkawi. |
Abstract:
UC Riverside research on nanolasers promise an explosion of memory capacity
The Library of Congress in Your Wrist Watch?
RIVERSIDE, CA | Posted on December 22nd, 2007Every advance in memory storage devices presents a new marvel of just how much memory can be squeezed into very small spaces. Considering the potential of nanolasers being developed in Sakhrat Khizroev's lab at the University of California, Riverside, things are about to get a lot smaller.
As reported in the latest issue of Technology Review, Khizroev is leading a team exploring lasers so tiny that they point to a future where a 10-terabit hard drive is only one-inch square.
That is 50 times the data density of today's magnetic storage technology, a technology that has nearly reached its limit for continued miniaturization. In response, researchers have been looking for a new leap forward by combining light and magnetism to focus bits of data on much smaller areas on the disk. The $60 billion a year hard disk drive industry is investigating several new technologies, one of which requires precise nanolasers to help "write" data.
Khizroev, an associate professor of engineering at UCR, and colleagues at the University of Houston led by Professor Dmitri Litvinov, have for the first time achieved a nanolaser which can concentrate light as small as 30 nanometers. For many substances, that is the molecular level. Just as importantly, their nanolaser can focus 250 nanowatts of power, enough to assure effective storage of the information.
The next goal of the researchers is to refine the nanolaser to produce light beams as small as five or 10 nanometers. To achieve this they plan to improve the manufacture of their nanolasers by refining the precision of the focused gallium ion beams used for their fabrication. Khizroev's lab adapted this technology, commonly used for diagnostics in semiconductor manufacture, to cut the components of their lasers.
He credited the feasibility of this advanced nanomanufacturing on Professor Robert Haddon's unique nanofabrication facilities at UCR's Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering.
Khizroev said there are a number of challenges for getting the tiny disk drives to the market, including lubricating tiny parts and integrating the nanolaser with a recording head. Still, he insisted, the 10-terabit hard drive will be a near-term innovation, appearing in as little as two years.
The implications of the ability to focus light at these scales are even more fantastic in the longer term. The use of photochromic proteins with nanolasers should help lead to nanocomputers and the ability to store still more data in smaller places, Khizroev said. Those proteins paired with nanolasers should also impact energy harvesting and a wide range of medical applications, he added.
####
About University of California, Riverside
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment of about 17,000 is projected to grow to 21,000 students by 2010. The campus is planning a medical school and already has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Graduate Center. With an annual statewide economic impact of nearly $1 billion, UCR is actively shaping the region's future. To learn more, visit www.ucr.edu or call (951) UCR-NEWS.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
News Media Contact:
Kris Lovekin
951.827.2495
Jim Dexter
951.827.2532
Copyright © University of California, Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








