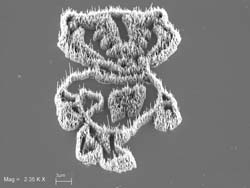
NanoBucky!
August 29, 2005
A team of chemistry researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison has put a new twist on an old philosophical riddle: How many Bucky Badger mascots can you fit on the head of a pin?
The answer: 9,000, with a little help from nanotechnology.
NanoBucky, created in the research lab of UW-Madison chemistry professor Robert J. Hamers, is composed of tiny carbon nanofiber "hairs," each just 75 nanometers in diameter. (A nanometer is equivalent to 1 billionth of a meter.) NanoBucky provides an entertaining illustration of the astounding scale under which nanotechnology pioneers ply their trade.
The nanofibers, one of several nanostructured forms of carbon developed in the last several years, have numerous potential applications and could play a role in the development of such things as tiny sensors for detecting chemical and biological agents. They may also have use in energy storage applications such as capacitors and lithium-ion batteries.
The fibers, and NanoBucky, are "grown" in a plasma deposition chamber where a mix of acetylene and ammonia gas are used with electrical current to prompt the growth of the nanofibers on a silicon substrate patterned with a nickel catalyst. The pattern for the catalyst is composed on a computer and is then traced on the substrate by a beam of electrons.
For more information on the fundamental science underlying NanoBucky, contact Hamers at (608) 262-6371; hamers@chem.wisc.edu
Terry Devitt
(608) 262-8282
trdevitt@wisc.edu
Copyright © University of Wisconsin-Madison
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||