Home > Nanotechnology Columns > NanoGlobe > OECD Addresses Business Environment for Nanotechnology & Its Impact on Energy & Medicine Commercialization - Part 2: Insight on OECD WPN Workshop on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Energy Option & Challenges in the Innovation Environment of Nanomedicine
 |
NanoGlobe Pte Ltd Nanotechnology Business Development Consultants NanoGlobe Pte Ltd |
Abstract:
This article highlights the discussions on the OECD workshops on nanoenergy and nanomedicine regarding to their business environment on aspects of R&D, financing, IP management, value chains and production, human resources, public perception, and EHS issues.
March 30th, 2010
OECD Addresses Business Environment for Nanotechnology & Its Impact on Energy & Medicine Commercialization - Part 2: Insight on OECD WPN Workshop on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Energy Option & Challenges in the Innovation Environment of Nanomedicine
The two workshops discussed the business environment for nanotechnology specifically in the application areas of energy and medicine. To continue our previous article, we summarize and highlight more details on the discussion and recommendations came out of the workshops. There were intensive discussions at the OECD Working Party on Nanotechnology (WPN) Workshop on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Energy Options (Nanoenergy workshop) and recommendations being made which are also applicable to the OECD WPN Workshop on Challenges in the Innovation Environment of Nanomedicine (Nanomedicine workshop). The priority technology areas in nanoenergy and nanomedicine are summarized in Table.1. Areas deserved most discussions in nanomedicine are early stage diagnostics and non-invasive therapeutics; and in nanoenergy are PV and batteries for electrical vehicles applications.
The challenges experienced at the commercialization pathway raised in the discussions of both workshops include:
1) Regulation to support and create nano market - government policy makers need to work closely with companies to full understand nanotechnology and the value it provides and create policy to support nanotech sustainable development.
2) Funding - for the full value chain of nanotech development including Proof of Concept, Proof of Value, supporting grow phase of company, international marketing and expansion
3) Public Private Partnership- encourage private sector to co-fund R&D and promote innovation; tech transfer mechanism/practices - interdisciplinary team, communication and capability development
4) Infrastructure support - enable access of world-class facilities and platform for industry and academia collaboration
5) Intellectual Property Right (IPR) - government could help sharing the costs of IP application and maintenance, regulate to encourage more innovation; collaborate with research institutes and reduce IP costs; build IP develop partnerships along the value chain; companies do not patent the keep trade secrets
6) Communication - being transparent, explain technology/products to the public through media and presentations at events/trade shows/exhibits (German Nano Truck, Taiwan Nano House; communicate with the regulatory body as early as the product concept was conceived
7) Information gaps - International Cooperation (database sharing, coordinate research efforts to avoid duplication), engage public communication
8) International cooperation and network - integrating global resources to allow access to infrastructures, financing, market, and manpower
9) Human Resource Development - internship programs nationally and internationally, HR mobility program
10) Form research and industry associations - to help with education, policy lobby, public acceptance, facilitate cooperation among players in different part of the value chain
11) Standardization and EHS Regulatory Issues - not enough information to regulate; no need to create new nanomedicine product regulation but integrate into the existing current regulatory pathway
Dr Bai Xu, CEO of Nanomed Devices, shared that "the world is flat, and globalization is rapidly growing in S& T development and global integration of resources would accelerate advancement of research and commercialization. Government needs to develop a balance strategy for facilitate academia and industry cooperation as the academia is long term looking, industry is shortsighted".
Taiwan stands out at the workshops for its very organized top down approach and developed infrastructures (at ITRI) for supporting commercialization.
I shared with the participants some of the unique government support mechanism in Singapore for facilitating nanotech commercialization in Singapore by attracting MNCs and SMEs from all over the world by building antechnology and industry ecosystem and international internship programs.
I am impressed by the leadership of Austria in setting up the European Center for Nanotoxicology based in Graz and the Austrian government is leading the WPN Nanomedicine project to explore challenges specific in nanomedicine and to identify global trends in key success factors and key barriers.
Italy stands out for its government support for setting up the European nanomedicine center in Lombardia.
Thailand shows its ambition in advancing its medical tourism through nanomedicine.
The panelists stressed that global R&D and business network is instrumental for nanotech industry growth allowing access to resources including infrastructure, manpower, funding, IP and market.
A number of participating economies shared their public private partnership practices especially in co-funding schemes and open infrastructure access. Israel and Singapore seem to provide attractive incentives (up 85% co-funding from government) for nanoenergy and nanomedicine incubation phase R&D. Singapore government (IE Singapore) also provides funding for grow phase companies especially with their international business development and expansion.
Both MNC and SME representatives share their practices in close partnerships among companies in the full industry value chain.
Cima Nanotech shared its superior platform technology (in making flexible transparent conductive thin film with Nano silver) that provides simpler, cheaper and green manufacturing process to replace the existing costly processes and materials (such as ITO).
Bayer Materials Science led the CNT Industry Consortium in Germany shared its full value chain cooperation strategy in accelerating CNT commercialization and sustainable development of nanotechnology.
The participants also stressed the importance of promoting closer collaboration between the developing and developed world.
The panel recommended that OECD could facilitate policy in Standard and EHS issues, IP protection hindering innovation issues, and creating nanomarket.
The event concluded with the approval of the Austria's proposed nanomedicine project by the WPN committee members.
Appendix:
Table 1 indicates the technology areas discussed at the two workshops. We summarize in Table 2 the challenges and recommendations made during the presentations and panel discussions at both workshops and highlight discussions and recommendations in Table 3 provided by representatives from different economies and organizations.
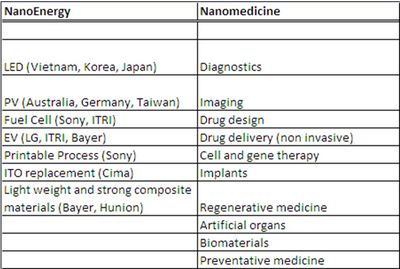 |
| Table 1- Technology Areas discussed in the OECD WPN Nanoenergy and Nanomedicine workshops |
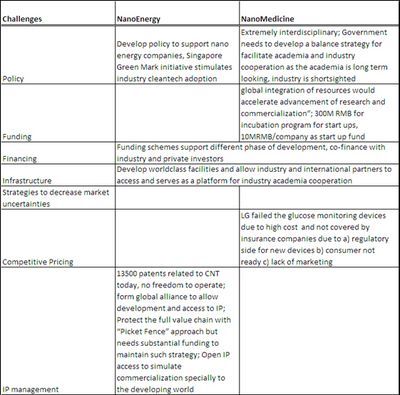 |
| Table 2- Highlights of discussions and recommendations provided at the OECD WPN Nanoenergy and Nanomedicine workshops on the key challenges of nanotechnology commercialization |
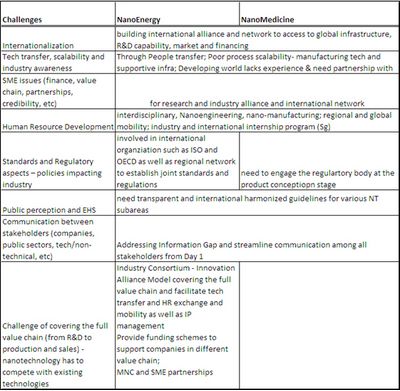 |
| Table 2 - continued |
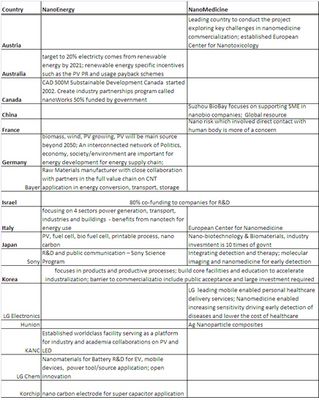 |
| Table 3-Highlights of discussions and recommendations provided at the OECD WPN Nanoenergy and Nanomedicine workshops by representatives from different economies and organizations on the key challenges of nanotechnology commercialization |
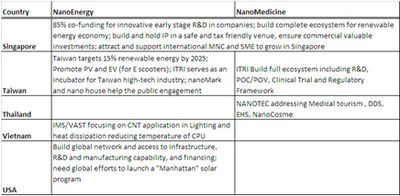 |
| Table 3 - continued |
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








