Home > Press > Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene
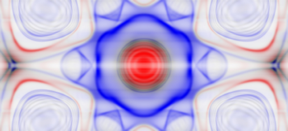 |
| Using density functional theory and measurement data from spin-resolved photoemission, the team investigated the origin of the repeating Au(111) bands and resolved them as deep surface resonances. These resonances lead to an onion-like Fermi surface of Au(111). CREDIT HZB |
Abstract:
Graphene consists of carbon atoms that crosslink in a plane to form a flat honeycomb structure. In addition to surprisingly high mechanical stability, the material has exciting electronic properties: The electrons behave like massless particles, which can be clearly demonstrated in spectrometric experiments. Measurements reveal a linear dependence of energy on momentum, namely the so-called Dirac cones - two lines that cross without a band gap - i.e. an energy difference between electrons in the conduction band and those in the valence bands.
Buckyballs on gold are less exotic than graphene
Berlin, Germany | Posted on July 22nd, 2022Variants in graphene architecture
Artificial variants of graphene architecture are a hot topic in materials research right now. Instead of carbon atoms, quantum dots of silicon have been placed, ultracold atoms have been trapped in the honeycomb lattice with strong laser fields, or carbon monoxide molecules have been pushed into place on a copper surface piece by piece with a scanning tunneling microscope, where they could impart the characteristic graphene properties to the electrons of the copper.
Artificial graphene with buckyballs?
A recent study suggested that it is infinitely easier to make artificial graphene using C60 molecules called buckyballs. Only a uniform layer of these needs to be vapor-deposited onto gold for the gold electrons to take on the special graphene properties. Measurements of photoemission spectra appeared to show a kind of Dirac cone.
Analysis of band structures at BESSY II
"That would be really quite amazing," says Dr. Andrei Varykhalov, of HZB, who heads a photoemission and scanning tunneling microscopy group. "Because the C60 molecule is absolutely nonpolar, it was hard for us to imagine how such molecules would exert a strong influence on the electrons in the gold." So Varykhalov and his team launched a series of measurements to test this hypothesis.
In tricky and detailed analyses, the Berlin team was able to study C60 layers on gold over a much larger energy range and for different measurement parameters. They used angle-resolved ARPES spectroscopy at BESSY II, which enables particularly precise measurements, and also analysed electron spin for some measurements.
Normal behavior
"We see a parabolic relationship between momentum and energy in our measured data, so it's a very normal behavior. These signals come from the electrons deep in the substrate (gold or copper) and not the layer, which could be affected by the buckyballs," explains Dr. Maxim Krivenkov, lead author of the study. The team was also able to explain the linear measurement curves from the previous study. "These measurement curves merely mimic the Dirac cones; they are an artifact, so to speak, of a deflection of the photoelectrons as they leave the gold and pass through the C60 layer," Varykhalov explains. Therefore, the buckyball layer on gold cannot be considered an artificial graphene.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Antonia Roetger
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
Office: 0049-308-062-43733
Expert Contact
Dr. Maxim Krivenkov
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








