Home > Press > Crystal phase engineering offers glimpse of future potential, researchers say
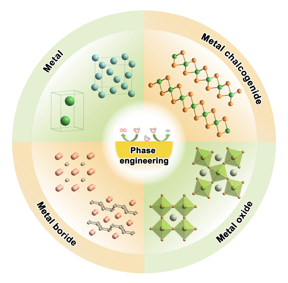 |
| With two decades of focused attention on how regulating such rearrangements, a process called phase engineering may enable sustainable energy conversion processes. CREDIT Nano Research, Tsinghua University Press |
Abstract:
Atomic rearrangement changes a material’s physical and chemical properties, which may lead to potential applications across disciplines, including in sustainable energy. With two decades of focused attention on how regulating such rearrangements, a process called phase engineering, may enable sustainable energy conversion processes, researchers in China have summarized the work so far, including how the field might progress.
Crystal phase engineering offers glimpse of future potential, researchers say
Beijing, China | Posted on July 15th, 2022They published their review on July 11 in Nano Research, with a specific focus on electrocatalysts. These materials trigger, enhance or resolve the chemical and electrical reactions involved in converting energy into storable or usable formats. They often serve as an electrode or as an electrode component.
“Phase engineering is an important strategy for designing efficient electrocatalysts toward these energy conversions, because it enables all catalytically active atoms to rearrange and form new lattices,” said co-corresponding author Xiaoxin Zou, professor, State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Jilin University. “This provides great opportunity to rationally manipulate atoms to discover attractive structural frameworks and to achieve better electrocatalysis. And while, in recent years, several researchers have summarized the preparation of nanomaterials with novel arrangements, this is the first systematic review toward rationalizing how these phases influence electrocatalytic activity.”
These various atomic arrangements are known as crystal phases. By changing how the atoms are arranged on the surface of a solid material, or in its bulk, can drastically change what the material can do. Zou noted, however, that the surface is essentially an extension of the bulk and cannot exist independently, so their connection is key to developing desirable and stable electrocatalysts.
“The underlying logic of phase engineering lies in an intimate relationship between the properties of the surface and of the bulk of a catalyst,” Zou said. “Engineering the bulk phase of a catalyst, which directly influences the surface, is a powerful strategy to design smart catalysts both internally and externally.”
The crystal structure of the bulk determines the material’s electronic structure, its conductivity and, largely, the composition of the surface layer. Different bulk crystal structures possess different characteristics and surface energies, leading to diverse morphology and catalytically active sites. Even for catalysts that experience significant surface damage or reconstruction during the catalysis process, Zou said, the bulk’s initial crystal structure strongly influences reconstitution and the final structure of the surface.
Over the last 20 years, several researchers have investigated this relationship, exploring unconventional electrocatalytic phases and how to induce such transformations. Driven by the demand for sustainable energy conversion processes, such as nitrogen fixation and carbon dioxide reduction, researchers advanced characterization techniques, as well as the theory underlying experimental work.
“These things made it possible to precisely and accurately understand the effects of crystal phases on electrocatalytic performance,” Zou said. "So, it is time to summarize phase engineering-related research that helps unravel phase-performance relationships and refines prediction in electrocatalysis studies.”
Next, Zou and his team recommend that researchers pursue four main areas to further advance crystal phase engineering for catalysis research.
“To develop competent catalysts for different energy conversion processes from a phase focus, we propose exploring the relationship between the crystal phase and catalytic activity levels; combining phase engineering with other design strategies; unraveling the formation and evolution mechanisms of unconventional phases; and enriching catalytic research of more fluid phases,” Zou said.
Contributors include Hui Chen, Mingcheng Zhang, Ke Sun, Lina Wang, Zhoubing Xie, Yucheng Shen, Xindi Han and Lan Yang, State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Jilin University; and Yanfei Wang, Petrochina Petrochemical Research Institute.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan, the Science and Technology Research Program of Education Department of Jilin Province and the 111 Project supported this research.
####
About Tsinghua University Press
Nano Research is a peer-reviewed, international and interdisciplinary research journal, sponsored by Tsinghua University and the Chinese Chemical Society. It offers readers an attractive mix of authoritative and comprehensive reviews and original cutting-edge research papers. After more than 10 years of development, it has become one of the most influential academic journals in the nano field. Rapid review to ensure quick publication is a key feature of Nano Research. In 2022 InCites Journal Citation Reports, Nano Research has an Impact Factor of 10.269 (9.136, 5 years), the total cites reached 29620, ranking first in China's international academic journals, and the number of highly cited papers reached 120, ranked among the top 2.8% of over 9000 academic journals.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yao Meng
Tsinghua University Press
Office: 86-108-347-0574
Copyright © Tsinghua University Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








