Home > Press > Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios—are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics?
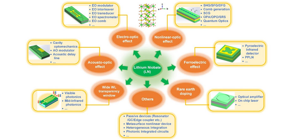 |
| Lithium niobate based devices covering electro-optic, nonlinear, ferroelectric, acousto-optic, visible, rare earth doping devices, etc. Credit: G. Chen et al., doi 10.1117/1.AP.4.3.034003. |
Abstract:
Lithium niobate (LiNbO3, LN) is one of the most important artificial materials and has been widely used in the photonics area since it was firstly discovered to have a ferroelectric property in 1949. Compared with other material systems, LN has various superior characteristics, such as a wide transparency window (400 nm to 5 m), large electro-optic (EO)/nonlinear-optic (NLO)/acousto-optic (AO)/pyroelectric coefficients, as well as stable chemical and physical properties. Based on these effects, various kinds of photonic devices have been demonstrated. For example, the large EO property of LN can be used for the realization of high-speed modulators.
Advances in lithium niobate photonics: High performance integrated LN-based photonic devices have developed rapidly in recent years, and many different structures have been demonstrated for various application scenarios—are we about to enter a new era of LN photonics?
Bellingham WA | Posted on June 24th, 2022In typical bulk LN (planar devices), light is confined inside a planar waveguide formed by ion-in diffusion or proton exchange. In such a method, the refractive index contrast is usually very small (~ 0.02), therefore bulk LN based devices have a large feature size and relatively poor performance even though they have been successfully used for decades. The problem of poor index contrast hampers further development of LN photonics as high power and large device sizes are not compatible with desired trends in energy efficiency and integration.
This situation may yet change, though, as high-quality thin film LN (TFLN) with controlled thickness has become available through the lapping and polishing and crystal ion slicing (CIS) methods. These high quality TFLNs can be bonded onto an insulator with a lower refractive index (such as silicon oxide), and then an LN on insulator (LNOI) structure similar to silicon on insulator (SOI) is realized.
The principal benefit from the large refractive index contrast of LNOI is that much more compact devices can be integrated on the same single chip by patterning structures using various developed etching technologies. In addition, TFLN can also be bonded to other material platforms which are lithographically patterned, where LN serves as a thin layer of unpatterned film and the light from waveguides or devices fabricated in the bonded platform interact with it. Relying on developed processing technologies, LN based photonic devices with high-performance, especially integrated devices, have experienced rapid development in recent years and many different structures for various application scenarios have been demonstrated. An era of LN photonics is coming.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS), Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), and Nanyang Technological University (NTU) recently summarized advances in LN photonics in detail. The content of this review, published in Advanced Photonics, includes the integrated LN photonics devices which have appeared in recent years, as well as selected bulk LN based devices and related processing technologies. In this way, the research community can reach a better, comprehensive understanding of the technology evolution of LN photonics.
On behalf of his team and the rapidly advancing field of research, Aaron J. Danner, NUS associate professor and senior author of the work, hopes readers may be inspired by this work and then contribute to the further development of LN photonics.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Daneet Steffens
SPIE--International Society for Optics and Photonics
Office: 360-685-5478
Copyright © SPIE--International Society for Optics and Photonics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








